Modulatory effects of cAMP and PKC activation on gap junctional intercellular communication among thymic epithelial cells
- PMID: 20078861
- PMCID: PMC2823718
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-3
Modulatory effects of cAMP and PKC activation on gap junctional intercellular communication among thymic epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: We investigated the effects of the signaling molecules, cyclic AMP (cAMP) and protein-kinase C (PKC), on gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) between thymic epithelial cells (TEC).
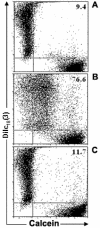
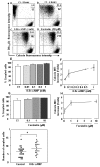
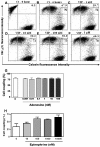
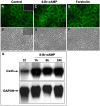
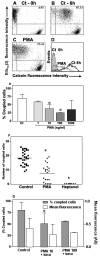
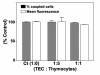
Results: Treatment with 8-Br-cAMP, a cAMP analog; or forskolin, which stimulates cAMP production, resulted in an increase in dye transfer between adjacent TEC, inducing a three-fold enhancement in the mean fluorescence of coupled cells, ascertained by flow cytometry after calcein transfer. These treatments also increased Cx43 mRNA expression, and stimulated Cx43 protein accumulation in regions of intercellular contacts. VIP, adenosine, and epinephrine which may also signal through cyclic nucleotides were tested. The first two molecules did not mimic the effects of 8-Br-cAMP, however epinephrine was able to increase GJIC suggesting that this molecule functions as an endogenous inter-TEC GJIC modulators. Stimulation of PKC by phorbol-myristate-acetate inhibited inter-TEC GJIC. Importantly, both the enhancing and the decreasing effects, respectively induced by cAMP and PKC, were observed in both mouse and human TEC preparations. Lastly, experiments using mouse thymocyte/TEC heterocellular co-cultures suggested that the presence of thymocytes does not affect the degree of inter-TEC GJIC.
Conclusions: Overall, our data indicate that cAMP and PKC intracellular pathways are involved in the homeostatic control of the gap junction-mediated communication in the thymic epithelium, exerting respectively a positive and negative role upon cell coupling. This control is phylogenetically conserved in the thymus, since it was seen in both mouse and human TEC preparations. Lastly, our work provides new clues for a better understanding of how the thymic epithelial network can work as a physiological syncytium.
Figures
References
-
- Loewenstein WR. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981;61:829–913. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

