Human coronavirus NL63 open reading frame 3 encodes a virion-incorporated N-glycosylated membrane protein
- PMID: 20078868
- PMCID: PMC2819038
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-6
Human coronavirus NL63 open reading frame 3 encodes a virion-incorporated N-glycosylated membrane protein
Abstract
Background: Human pathogenic coronavirus NL63 (hCoV-NL63) is a group 1 (alpha) coronavirus commonly associated with respiratory tract infections. In addition to known non-structural and structural proteins all coronaviruses have one or more accessory proteins whose functions are mostly unknown. Our study focuses on hCoV-NL63 open reading frame 3 (ORF 3) which is a highly conserved accessory protein among coronaviruses.
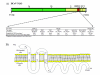
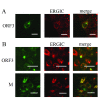
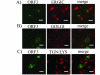
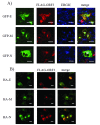
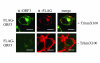
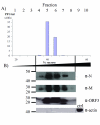
Results: In-silico analysis of the 225 amino acid sequence of hCoV-NL63 ORF 3 predicted a triple membrane-spanning protein. Expression in infected CaCo-2 and LLC-MK2 cells was confirmed by immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis. The protein was detected within the endoplasmatic reticulum/Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) where coronavirus assembly and budding takes place. Subcellular localization studies using recombinant ORF 3 protein transfected in Huh-7 cells revealed occurrence in ERGIC, Golgi- and lysosomal compartments. By fluorescence microscopy of differently tagged envelope (E), membrane (M) and nucleocapsid (N) proteins it was shown that ORF 3 protein colocalizes extensively with E and M within the ERGIC. Using N-terminally FLAG-tagged ORF 3 protein and an antiserum specific to the C-terminus we verified the proposed topology of an extracellular N-terminus and a cytosolic C-terminus. By in-vitro translation analysis and subsequent endoglycosidase H digestion we showed that ORF 3 protein is N-glycosylated at the N-terminus. Analysis of purified viral particles revealed that ORF 3 protein is incorporated into virions and is therefore an additional structural protein.
Conclusions: This study is the first extensive expression analysis of a group 1 hCoV-ORF 3 protein. We give evidence that ORF 3 protein is a structural N-glycosylated and virion-incorporated protein.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential maturation and subcellular localization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus surface proteins S, M and E.J Gen Virol. 2005 May;86(Pt 5):1423-1434. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.80671-0. J Gen Virol. 2005. PMID: 15831954
-
The structural and accessory proteins M, ORF 4a, ORF 4b, and ORF 5 of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) are potent interferon antagonists.Protein Cell. 2013 Dec;4(12):951-61. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-3096-8. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 24318862 Free PMC article.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 envelope and membrane proteins modulate maturation and retention of the spike protein, allowing assembly of virus-like particles.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100111. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016175. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33229438 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2.Malays J Pathol. 2020 Apr;42(1):3-11. Malays J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32342926 Review.
-
[Basic information of Coronavirus].Uirusu. 2020;70(1):29-36. doi: 10.2222/jsv.70.29. Uirusu. 2020. PMID: 33967109 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infected human cell lines identifies HSP90 as target for COVID-19 therapy.iScience. 2021 Mar 19;24(3):102151. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102151. Epub 2021 Feb 6. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33585804 Free PMC article.
-
Human coronaviruses: activation and antagonism of innate immune responses.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025 Mar 27;89(1):e0001623. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00016-23. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39699237 Review.
-
Identification of host cell proteins that interact with the M protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus.Vet Microbiol. 2020 Jul;246:108729. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108729. Epub 2020 May 21. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32605758 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Human Coronavirus HCoV-NL63.Open Virol J. 2010 May 25;4:76-84. doi: 10.2174/1874357901004010076. Open Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20700397 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Whole-Virus ELISA for Serological Evaluation of Domestic Livestock as Possible Hosts of Human Coronavirus NL63.Viruses. 2019 Jan 9;11(1):43. doi: 10.3390/v11010043. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30634419 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

