Lasting immune memory against hepatitis B in children after primary immunization with 4 doses of DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib in the first and 2nd year of life
- PMID: 20078876
- PMCID: PMC2821389
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-9
Lasting immune memory against hepatitis B in children after primary immunization with 4 doses of DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib in the first and 2nd year of life
Abstract
Background: Few studies have assessed long term persisting immunity against hepatitis B virus (HBV) in children vaccinated during infancy with combined vaccines containing recombinant HBV surface antigen (HBs). We assessed antibody persistence and immune memory in children 4-5 years of age, previously vaccinated with four doses of combined hexavalent DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib vaccine (Infanrix hexa).
Methods: Immune memory was assessed in 301 children through administration of a challenge dose of monovalent HBV vaccine.
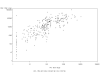
Results: At 4-5 years of age, 85.3% of subjects had persisting anti-HBs antibody concentrations >or= 10 mIU/mL, rising to 98.6% after the HBV challenge dose. All but 12 subjects (95.8%) achieved post-challenge anti-HBs concentrations >or= 100 mIU/mL. The post-challenge anti-HBs GMC rose by 100-fold compared to pre-challenge concentrations. An anamnestic response to the HBV vaccine challenge was observed in 96.8% of subjects, including 17/21 (81.0%) of children with initially undetectable antibodies (<3.3 mIU/mL). All but 4 of 42 subjects (90.5%) with anti-HBs antibodies <10 mIU/mL prior to the challenge dose, achieved seroprotective levels afterwards. A 4-fold rise in antibody concentration after the challenge dose was observed in 259/264 (98.1%) of initially seropositive subjects. The magnitude of the post-challenge responses was proportional to pre-challenge anti-HBs levels. No serious adverse events were reported during the study.
Conclusion: The combined DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib vaccine induced lasting immune memory against hepatitis B. Long term protection afforded by DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib is likely to be similar to that observed following priming with monovalent HBV vaccines.
Trial registration: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov 106789 NCT00411697.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B vaccines WHO position paper. WER. 2004;79:255–263. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis B Virus: A comprehensive strategy for eliminating transmission in the United States through universal childhood vaccination: Recommendations of the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) MMWR. 1991;40(RR-13):1–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical