Crystal structure of mouse Elf3 C-terminal DNA-binding domain in complex with type II TGF-beta receptor promoter DNA
- PMID: 20079749
- PMCID: PMC2830650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.017
Crystal structure of mouse Elf3 C-terminal DNA-binding domain in complex with type II TGF-beta receptor promoter DNA
Abstract
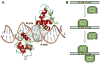
The Ets family of transcription factors is composed of more than 30 members. One of its members, Elf3, is expressed in virtually all epithelial cells as well as in many tumors, including breast tumors. Several studies observed that the promoter of the type II TGF-beta receptor gene (TbetaR-II) is strongly stimulated by Elf3 via two adjacent Elf3 binding sites, the A-site and the B-site. Here, we report the 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of a mouse Elf3 C-terminal fragment, containing the DNA-binding Ets domain, in complex with the B-site of mouse type II TGF-beta receptor promoter DNA (mTbetaR-II(DNA)). Elf3 contacts the core GGAA motif of the B-site from a major groove similar to that of known Ets proteins. However, unlike other Ets proteins, Elf3 also contacts sequences of the A-site from the minor groove of the DNA. DNA binding experiments and cell-based transcription studies indicate that minor groove interaction by Arg349 located in the Ets domain is important for Elf3 function. Equally interesting, previous studies have shown that the C-terminal region of Elf3, which flanks the Ets domain, is required for Elf3 binding to DNA. In this study, we determined that Elf3 amino acid residues within this flanking region, including Trp361, are important for the structural integrity of the protein as well as for the Efl3 DNA binding and transactivation activity.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Unique and selective effects of five Ets family members, Elf3, Ets1, Ets2, PEA3, and PU.1, on the promoter of the type II transforming growth factor-beta receptor gene.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 7;279(19):19407-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M314115200. Epub 2004 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14976186
-
Preliminary crystallographic analysis of mouse Elf3 C-terminal DNA-binding domain in complex with type II TGF-beta receptor promoter DNA.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009 Dec 1;65(Pt 12):1261-3. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109038007. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009. PMID: 20054123 Free PMC article.
-
Different domains of the transcription factor ELF3 are required in a promoter-specific manner and multiple domains control its binding to DNA.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 2;282(5):3027-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609907200. Epub 2006 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17148437
-
Regulation of Ets function by protein - protein interactions.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 18;19(55):6514-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204035. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11175367 Review.
-
Structural and functional analysis of domains of the progesterone receptor.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 30;348(2):418-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.07.017. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21803119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the ETS domain of human Ergp55 in complex with the cfos promoter DNA sequence.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012 Nov 1;68(Pt 11):1333-6. doi: 10.1107/S1744309112038675. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012. PMID: 23143243 Free PMC article.
-
Structural modeling and DNA binding autoinhibition analysis of Ergp55, a critical transcription factor in prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039850. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761914 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative structure analysis of the ETSi domain of ERG3 and its complex with the E74 promoter DNA sequence.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2018 Oct 1;74(Pt 10):656-663. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X1801110X. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2018. PMID: 30279318 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of ETS-family DNA-binding in vitro and in vivo.EMBO J. 2010 Jul 7;29(13):2147-60. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.106. Epub 2010 Jun 1. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20517297 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of ESE-1 subdomains required to initiate mammary epithelial cell transformation via a cytoplasmic mechanism.Mol Cancer. 2011 Aug 28;10:103. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-103. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21871131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kopp JL, Wilder PJ, Desler M, Kinarsky L, Rizzino A. Different domains of the transcription factor ELF3 are required in a promoter-specific manner and multiple domains control its binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:3027–41. - PubMed
-
- Eckel KL, Tentler JJ, Cappetta GJ, Diamond SE, Gutierrez-Hartmann A. The epithelial-specific ETS transcription factor ESX/ESE-1/Elf-3 modulates breast cancer-associated gene expression. DNA Cell Biol. 2003;22:79–94. - PubMed
-
- Chang J, Lee C, Hahm KB, Yi Y, Choi SG, Kim SJ. Over-expression of ERT(ESX/ESE-1/ELF3), an ets-related transcription factor, induces endogenous TGF-beta type II receptor expression and restores the TGF-beta signaling pathway in Hs578t human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2000;19:151–4. - PubMed
-
- Rudders S, Gaspar J, Madore R, Voland C, Grall F, Patel A, Pellacani A, Perrella MA, Libermann TA, Oettgen P. ESE-1 is a novel transcriptional mediator of inflammation that interacts with NF-kappa B to regulate the inducible nitric-oxide synthase gene. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:3302–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

