Role of the UL45 protein in herpes simplex virus entry via low pH-dependent endocytosis and its relationship to the conformation and function of glycoprotein B
- PMID: 20080138
- PMCID: PMC2834853
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.01.004
Role of the UL45 protein in herpes simplex virus entry via low pH-dependent endocytosis and its relationship to the conformation and function of glycoprotein B
Abstract
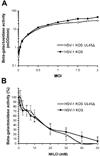
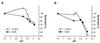
Herpesviruses commandeer distinct cellular pathways to enter target cells. The mechanism by which herpes simplex virus (HSV) selects a pH-dependent, endocytic route or a pH-independent route remains to be elucidated. We investigated the role of the non-glycosylated viral envelope protein UL45 in HSV entry via endocytosis. UL45 plays a role in mediating cell-cell fusion and has been proposed to functionally interact with gB to regulate membrane fusion. Thus, we also probed the impact of UL45 on the structure and function of gB present in virions. A UL45 deletion virus successfully entered cells via low pH, endocytic pathway with wild type kinetics. In the absence or presence of UL45, the antigenic conformation of virion gB appeared unaltered. Antibodies to gB neutralized infection of the UL45-deletion virus and wild type virus to a similar extent, regardless of whether the target cells supported low pH endocytic or non-endocytic entry routes. Lastly, HSV virions were inactivated by low pH regardless of the presence of UL45. The results, together with previous studies, suggest that UL45 plays distinct roles in cell-cell fusion and virus-cell fusion during acid-dependent entry.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

