Nasal absorption of mixtures of fast-acting and long-acting insulins
- PMID: 20080164
- PMCID: PMC2834479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.01.013
Nasal absorption of mixtures of fast-acting and long-acting insulins
Abstract
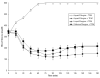
Mixtures of fast-acting and long-acting insulins were administered nasally to anesthetized, hyperglycemic rats in the presence and absence of tetradecyl-beta-d-maltoside (TDM). The fast-acting analogs, aspart insulin, lispro insulin and glulisine insulin, were all rapidly absorbed from the nose when applied individually with 0.125% TDM (T(max)=15min). One long-acting insulin analog, glargine insulin, was also absorbed from the nose when applied individually in the presence of 0.125% TDM (T(max)=60min). The other long-acting insulin analog, detemir insulin, was not soluble when formulated with 0.125% TDM. A series of mixtures (1:1) of the three rapid-acting insulins and long-acting glargine insulin were formulated with 0.125% TDM and applied nasally. The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of the insulin mixtures reflected the additive contributions of both the rapid-acting and the long-acting insulins. These results support the possibility of formulating certain insulin mixtures in tandem to provide nasal insulin products that match the needs of patients with diabetes mellitus better than those currently available.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
State of insulin self-association does not affect its absorption from the pulmonary route.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005 Jun;25(2-3):289-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2005.03.006. Epub 2005 Apr 11. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005. PMID: 15911225
-
Insulin analog preparations and their use in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Paediatr Drugs. 2008;10(3):163-76. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200810030-00005. Paediatr Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18454569 Review.
-
Reestablishment of the nasal permeability barrier to several peptides following exposure to the absorption enhancer tetradecyl-beta-D-maltoside.J Pharm Sci. 2010 Apr;99(4):1912-20. doi: 10.1002/jps.21977. J Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 19894270
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin lispro mixtures.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(13):1043-57. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241130-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12403642 Review.
-
Subcutaneous insulin: pharmacokinetic variability and glycemic variability.Diabetes Metab. 2005 Sep;31(4 Pt 2):4S7-4S24. doi: 10.1016/s1262-3636(05)88263-1. Diabetes Metab. 2005. PMID: 16389894 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Intranasal Insulin Aspart: A Profile of Gene Expression, Memory, and Insulin Receptors in Aged F344 Rats.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020 May 22;75(6):1021-1030. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glz105. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31180116 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Delivery to the Brain via the Nasal Route: Unraveling the Potential for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Jul;14(7):1776-1793. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01558-1. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38441832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative pharmacokinetic studies of borneol in mouse plasma and brain by different administrations.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2012 Dec;13(12):990-6. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1200142. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2012. PMID: 23225854 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Insulin Improves Age-Related Cognitive Deficits and Reverses Electrophysiological Correlates of Brain Aging.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016 Jan;71(1):30-9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu314. Epub 2015 Feb 6. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 25659889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahsan F, Arnold JJ, Yang T, Meezan E, Schwiebert EM, Pillion DJ. Effects of the permeability enhancers, tetradecylmaltoside and dimethyl-B-cyclodextrin, on insulin movement across human bronchial epithelial cells 16HBE 14o. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2003;20:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Arnold JJ. Doctoral Dissertation. University of Alabama at Birmingham; 2004. Systemic Delivery of Peptides and Macromolecules in Nasal Formulations Containing an Alkylglycoside.
-
- Arnold JJ, Ahsan F, Meezan E, Pillion DJ. Nasal administration of low molecular weight heparin. J Pharm Sci. 2002;91(7):1707–14. - PubMed
-
- Arnold JJ, Ahsan F, Meezan E, Pillion DJ. Correlation of tetradecylmaltoside induced increase in nasal peptide drug delivery with morphological changes in nasal epithelial cells. J Pharmaceut Sci. 2004;93:2205–2213. - PubMed
-
- Arnold JJ, Fyrberg MD, Meezan E, Pillion DJ. Reestablishment of the Nasal Permeability Barrier to Several Peptides Following Exposure to the Absorption Enhancer Tetradecyl-β-D-Maltoside. J Pharmaceut Sci. 2009 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

