Anti-inflammatory effect of a selective IkappaB kinase-beta inhibitor in rat lung in response to LPS and cigarette smoke
- PMID: 20080200
- PMCID: PMC2850968
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.01.002
Anti-inflammatory effect of a selective IkappaB kinase-beta inhibitor in rat lung in response to LPS and cigarette smoke
Abstract
Rationale: IkappaB kinase (IKK) activates NF-kappaB which plays a pivotal role in pro-inflammatory response in the lung. NF-kappaB has been shown to be activated in alveolar macrophages and peripheral lungs of smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. We investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of a highly selective and novel IKKbeta/IKK2 inhibitor, PHA-408 [8-(5-chloro-2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)isonicotinamido)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-benzo[gamma]indazole-3-carboxamide], in lungs of rat in vivo.
Methods: Adult Sprague-Dawley rats were administered orally with PHA-408 (15 and 45 mg/kg) daily for 3 days and exposed to LPS aerosol (once on day 3, 2 h post-last PHA-408 administration) or cigarette smoke (CS; 2h after PHA-408 administration for 3 days). Animals were sacrificed at 1, 4 and 24 h after the last exposure, and lung inflammatory response and NF-kappaB activation were measured.
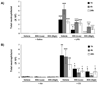
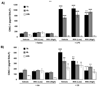
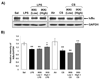
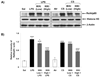
Results: Oral administration of IKKbeta/IKK2 inhibitor PHA-408 significantly inhibited LPS- and CS-mediated neutrophil influx in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of rats. The levels of pro-inflammatory mediators in BAL fluid (CINC-1) and lungs (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and GM-CSF) were also reduced by PHA-408 administration in response to LPS or CS exposures. The reduced pro-inflammatory response in PHA-408-administered rats was associated with decreased nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity of NF-kappaB in response to LPS or CS.
Conclusion: These results suggest that IKKbeta/IKK2 inhibitor PHA-408 is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent against LPS- and CS-mediated lung inflammation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Novel tight-binding inhibitory factor-kappaB kinase (IKK-2) inhibitors demonstrate target-specific anti-inflammatory activities in cellular assays and following oral and local delivery in an in vivo model of airway inflammation.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Aug;330(2):377-88. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.147538. Epub 2009 May 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19478133
-
A novel, highly selective, tight binding IkappaB kinase-2 (IKK-2) inhibitor: a tool to correlate IKK-2 activity to the fate and functions of the components of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in arthritis-relevant cells and animal models.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Apr;329(1):14-25. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.143800. Epub 2009 Jan 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19168710
-
Baicalin attenuates inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation in cigarette smoke induced inflammatory models.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Oct;23(5):411-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.05.004. Epub 2010 May 23. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20566376
-
Targeted disruption of NF-{kappa}B1 (p50) augments cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema in mice: a critical role of p50 in chromatin remodeling.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):L197-209. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00265.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19965984 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of polymixin B on I-kappaB kinase mRNA expression in lipopolysaccharide- induced pulmonary alveolar macrophages].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2003 Jul;15(7):429-31. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2003. PMID: 12857501 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Progress in the mechanism and targeted drug therapy for COPD.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Oct 27;5(1):248. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00345-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 33110061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cigarette smoke induced airway inflammation is independent of NF-κB signalling.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054128. Epub 2013 Jan 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349803 Free PMC article.
-
αVβ3 integrin regulates macrophage inflammatory responses via PI3 kinase/Akt-dependent NF-κB activation.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Feb;226(2):469-76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22356. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20672329 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling and targeted proteomics reveals common molecular changes associated with cigarette smoke-induced lung emphysema development in five susceptible mouse strains.Inflamm Res. 2015 Jul;64(7):471-86. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0820-2. Epub 2015 May 12. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25962837 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IKKβ in Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities for the Therapeutic Utilisation of IKKβ Inhibitors.Cells. 2018 Aug 23;7(9):115. doi: 10.3390/cells7090115. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30142927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burchfiel CM, Marcus EB, Curb JD, Maclean CJ, Vollmer WM, Johnson LR, et al. Effects of smoking and smoking cessation on longitudinal decline in pulmonary function. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:1778–1785. - PubMed
-
- Saetta M. Airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:S17–S20. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Kleinert S. COPD--a neglected disease. Lancet. 2004;364:564–565. - PubMed
-
- Halbert RJ, Natoli JL, Gano A, Badamgarav E, Buist AS, Mannino DM. Global burden of COPD: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2006;28:523–532. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ, Hansel TT. Prospects for new drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2004;364:985–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

