Reducing the desire for cocaine with subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation
- PMID: 20080543
- PMCID: PMC2824319
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908189107
Reducing the desire for cocaine with subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation
Abstract
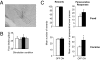
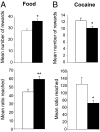
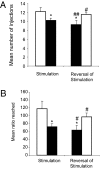
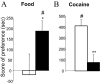
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a reversible technique that is currently used for the treatment of Parkinson disease and may be suitable for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Whether DBS inactivates the target structure is still a matter of debate. Here, from findings obtained in rats, we propose DBS of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) as a possible treatment for cocaine addiction to be further tested in human studies. We show that STN DBS reversibly reduces the motivation to work for an i.v. injection of cocaine, and it increases motivation to work for sucrose pellets. These opposite effects may result from STN DBS effect on the positive affective properties of these rewards. Indeed, we further show that STN DBS reduces the preference for a place previously associated with the rewarding properties of cocaine, and it increases the preference for a place associated with food. Because these findings are consistent with those observed after STN lesions [Baunez C, Dias C, Cador M, Amalric M (2005) Nat Neurosci 8:484-489], they suggest that STN DBS mimics an inactivation of the STN on motivational processes. Furthermore, given that one of the major challenges for cocaine addiction is to find a treatment that reduces the craving for the drug without diminishing the motivation for naturally rewarding activities, our findings validate STN as a good target and DBS as the appropriate technique for a promising therapeutic strategy in the treatment of cocaine addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Limousin P, et al. Effect of parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet. 1995;345:91–95. - PubMed
-
- Benabid AL. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:696–706. - PubMed
-
- Moro E, et al. Bilateral globus pallidus stimulation for Huntington’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2004;56:290–294. - PubMed
-
- Lozano AM, et al. Subcallosal cingulate gyrus deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64:461–467. - PubMed
-
- Mallet L, et al. STOC Study Group. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2121–2134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

