Functional diversity among a family of human skeletal muscle myosin motors
- PMID: 20080549
- PMCID: PMC2824297
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913527107
Functional diversity among a family of human skeletal muscle myosin motors
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 8;107(23):10765
Abstract
Human skeletal muscle fibers express five highly conserved type-II myosin heavy chain (MyHC) genes in distinct spatial and temporal patterns. In addition, the human genome contains an intact sixth gene, MyHC-IIb, which is thought under most circumstances not to be expressed. The physiological and biochemical properties of individual muscle fibers correlate with the predominantly expressed MyHC isoform, but a functional analysis of homogenous skeletal muscle myosin isoforms has not been possible. This is due to the difficulties of separating the multiple isoforms usually coexpressed in muscle fibers, as well as the lack of an expression system that produces active recombinant type II skeletal muscle myosin. In this study we describe a mammalian muscle cell expression system and the functional analysis of all six recombinant human type II skeletal muscle myosin isoforms. The diverse biochemical activities and actin-filament velocities of these myosins indicate that they likely have distinct functions in muscle. Our data also show that ATPase activity and motility are generally correlated for human skeletal muscle myosins. The exception, MyHC-IIb, encodes a protein that is high in ATPase activity but slow in motility; this is the first functional analysis of the protein from this gene. In addition, the developmental isoforms, hypothesized to have low ATPase activity, were indistinguishable from adult-fast MyHC-IIa and the specialized MyHC-Extraocular isoform, that was predicted to be the fastest of all six isoforms but was functionally similar to the slower isoforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
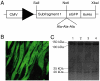
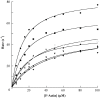
 F-actin. The datasets for each preparation of an isoform across a range of 0–
F-actin. The datasets for each preparation of an isoform across a range of 0– F-actin were fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation using KaleidaGraph.
F-actin were fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation using KaleidaGraph.Similar articles
-
Abundant expression of myosin heavy-chain IIB RNA in a subset of human masseter muscle fibres.Arch Oral Biol. 2001 Nov;46(11):1039-50. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9969(01)00066-8. Arch Oral Biol. 2001. PMID: 11543711 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized cranial muscles: how different are they from limb and abdominal muscles?Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(1-2):73-86. doi: 10.1159/000070576. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003. PMID: 12784043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of myosin isoforms in denervated, cross-reinnervated, and electrically stimulated rabbit muscles.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Mar 1;236(2):539-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.00539.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8612627
-
Myosin isoforms and muscle fiber characteristics in equine gluteus medius muscle.Anat Rec. 1996 Apr;244(4):444-51. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199604)244:4<444::AID-AR3>3.0.CO;2-V. Anat Rec. 1996. PMID: 8694280
-
Myosin isoforms in mammalian skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1994 Aug;77(2):493-501. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.77.2.493. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1994. PMID: 8002492 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of sequence changes in myosin II that adjust muscle contraction velocity.PLoS Biol. 2021 Jun 10;19(6):e3001248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001248. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 34111116 Free PMC article.
-
The superfast human extraocular myosin is kinetically distinct from the fast skeletal IIa, IIb, and IId isoforms.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 20;288(38):27469-27479. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.488130. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23908353 Free PMC article.
-
The myosin-binding UCS domain but not the Hsp90-binding TPR domain of the UNC-45 chaperone is essential for function in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Sci. 2011 Sep 15;124(Pt 18):3164-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.087320. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21914819 Free PMC article.
-
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle is spared from MuRF1-mediated muscle atrophy in mice with acute lung injury.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):e87587. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087587. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498144 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous mutations in human β, embryonic, and perinatal muscle myosins have divergent effects on molecular power generation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 27;121(9):e2315472121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315472121. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38377203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bottinelli R, Betto R, Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Maximum shortening velocity and coexistence of myosin heavy chain isoforms in single skinned fast fibres of rat skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1994;15:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Reiser PJ, Moss RL, Giulian GG, Greaser ML. Shortening velocity in single fibers from adult rabbit soleus muscles is correlated with myosin heavy chain composition. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:9077–9080. - PubMed
-
- Weiss A, Leinwand LA. The mammalian myosin heavy chain gene family. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:417–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

