HOXB9, a gene overexpressed in breast cancer, promotes tumorigenicity and lung metastasis
- PMID: 20080567
- PMCID: PMC2824265
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912710107
HOXB9, a gene overexpressed in breast cancer, promotes tumorigenicity and lung metastasis
Abstract
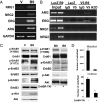
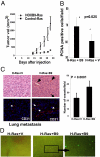
The mechanisms underlying tumoral secretion of signaling molecules into the microenvironment, which modulates tumor cell fate, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis, are not well understood. Aberrant expression of transcription factors, which has been implicated in the tumorigenesis of several types of cancers, may provide a mechanism that induces the expression of growth and angiogenic factors in tumors, leading to their local increase in the tumor microenvironment, favoring tumor progression. In this report, we demonstrate that the transcription factor HOXB9 is overexpressed in breast carcinoma, where elevated expression correlates with high tumor grade. HOXB9 induces the expression of several angiogenic factors (VEGF, bFGF, IL-8, and ANGPTL-2), as well as ErbB (amphiregulin, epiregulin, and neuregulins) and TGF-ss, which activate their respective pathways, leading to increased cell motility and acquisition of mesenchymal phenotypes. In vivo, HOXB9 promotes the formation of large, well-vascularized tumors that metastasize to the lung. Thus, deregulated expression of HOXB9 contributes to breast cancer progression and lung metastasis by inducing several growth factors that alter tumor-specific cell fates and the tumor stromal microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Homeodomain-containing protein HOXB9 regulates expression of growth and angiogenic factors, facilitates tumor growth in vitro and is overexpressed in breast cancer tissue.FEBS J. 2012 Oct;279(19):3715-3726. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08733.x. Epub 2012 Aug 31. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22863320 Free PMC article.
-
HOXB9 expression promoting tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis is associated with clinical outcomes in breast cancer patients.Ann Surg Oncol. 2012 Jun;19(6):1831-40. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2295-5. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22396001
-
An E2F1-HOXB9 transcriptional circuit is associated with breast cancer progression.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 19;9(8):e105285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105285. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25136922 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenesis, adipokines and breast cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009 Jun;20(3):193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009. PMID: 19520599 Review.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition for Breast Carcinogenesis.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 11;9(9):476. doi: 10.3390/biom9090476. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31514467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of HOX gene expression patterns in human breast cancer.Mol Biotechnol. 2014 Jan;56(1):64-71. doi: 10.1007/s12033-013-9682-4. Mol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 23820980
-
Sox2 promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells.EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Jan;6(1):66-79. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303411. EMBO Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24178749 Free PMC article.
-
Homeodomain-containing protein HOXB9 regulates expression of growth and angiogenic factors, facilitates tumor growth in vitro and is overexpressed in breast cancer tissue.FEBS J. 2012 Oct;279(19):3715-3726. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08733.x. Epub 2012 Aug 31. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22863320 Free PMC article.
-
PCAF-mediated acetylation of transcriptional factor HOXB9 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression by targeting oncogenic protein JMJD6.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 15;44(22):10662-10675. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw808. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27613418 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of HOXA13 as a potential tumorigenesis and progression promoter of LUSC based on qRT-PCR and bioinformatics.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):10650-10665. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abate-Shen C. Deregulated homeobox gene expression in cancer: Cause or consequence? Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:777–785. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Capecchi MR. Targeted mutations in hoxa-9 and hoxb-9 reveal synergistic interactions. Dev Biol. 1997;181:186–196. - PubMed
-
- Bodey B, Bodey B. Siegel SE, Kaiser HE., Jr. Immunocytochemical detection of the homeobox B3, B4, and C6 gene products in breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 20(5A):3281–3286. - PubMed
-
- Cantile M, et al. In vivo expression of the whole HOX gene network in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:257–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

