A mutation in the first intracellular loop of CACNA1A prevents P/Q channel modulation by SNARE proteins and lowers exocytosis
- PMID: 20080591
- PMCID: PMC2824376
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908359107
A mutation in the first intracellular loop of CACNA1A prevents P/Q channel modulation by SNARE proteins and lowers exocytosis
Abstract
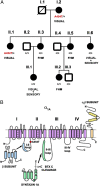
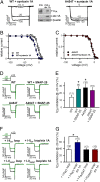
Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM)-causing mutations in the gene encoding the P/Q Ca(2+) channel alpha(1A) subunit (CACNA1A) locate to the pore and voltage sensor regions and normally involve gain-of-channel function. We now report on a mutation identified in the first intracellular loop of CACNA1A (alpha(1A(A454T))) that does not cause FHM but is associated with the absence of sensorimotor symptoms in a migraine with aura pedigree. Alpha(1A(A454T)) channels showed weakened regulation of voltage-dependent steady-state inactivation by Ca(V)beta subunits. More interestingly, A454T mutation suppressed P/Q channel modulation by syntaxin 1A or SNAP-25 and decreased exocytosis. Our findings reveal the importance of I-II loop structural integrity in the functional interaction between P/Q channel and proteins of the vesicle-docking/fusion machinery, and that genetic variation in CACNA1A may be not only a cause but also a modifier of migraine phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
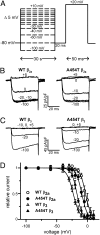
 , n = 22) –12.8 ± 0.5 and –5.1 ± 0.4; A454T (•, n = 14) –9.2 ± 0.5 and –4.6 ± 0.5; A454T + syntaxin 1A (
, n = 22) –12.8 ± 0.5 and –5.1 ± 0.4; A454T (•, n = 14) –9.2 ± 0.5 and –4.6 ± 0.5; A454T + syntaxin 1A ( , n = 15) –7.8 ± 0.5 and –4.8 ± 0.5. (D) Inhibition of WT and A454T P/Q channels alone (Left) or coexpressed with SNAP-25 (Right) evoked by a 20-ms test pulse to +20 mV following a 30-s prepulse to −80 mV (black trace) or −20 mV (green trace). (E) Average percentage ICa inhibition of WT and A454T P/Q channels in the absence or presence of SNAP-25. Ca2+ currents obtained as indicated in D were normalized to the current following the −80 mV prepulse. *P < 0.05 vs. WT. (F) Representative current traces from HEK 293 cells expressing WT P/Q channels coexpressed with WT (I-IIWT loop) or A454T (I-IIA545T loop) intracellular loops connecting domains I and II in the absence or presence of syntaxin 1A (stx 1A). Ca2+ currents were evoked by a 20-ms test pulse to +20 mV following a 30-s prepulse to −80 mV (black trace) or −20 mV (green trace). (G) Average percentage of WT P/Q ICa inhibition obtained under the experimental conditions shown in F (*P < 0.01).
, n = 15) –7.8 ± 0.5 and –4.8 ± 0.5. (D) Inhibition of WT and A454T P/Q channels alone (Left) or coexpressed with SNAP-25 (Right) evoked by a 20-ms test pulse to +20 mV following a 30-s prepulse to −80 mV (black trace) or −20 mV (green trace). (E) Average percentage ICa inhibition of WT and A454T P/Q channels in the absence or presence of SNAP-25. Ca2+ currents obtained as indicated in D were normalized to the current following the −80 mV prepulse. *P < 0.05 vs. WT. (F) Representative current traces from HEK 293 cells expressing WT P/Q channels coexpressed with WT (I-IIWT loop) or A454T (I-IIA545T loop) intracellular loops connecting domains I and II in the absence or presence of syntaxin 1A (stx 1A). Ca2+ currents were evoked by a 20-ms test pulse to +20 mV following a 30-s prepulse to −80 mV (black trace) or −20 mV (green trace). (G) Average percentage of WT P/Q ICa inhibition obtained under the experimental conditions shown in F (*P < 0.01).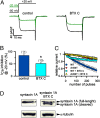

References
-
- Pietrobon D. Familial hemiplegic migraine. Neurotherapeutics. 2007;4:274–284. - PubMed
-
- Ducros A, et al. The clinical spectrum of familial hemiplegic migraine associated with mutations in a neuronal calcium channel. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:17–24. - PubMed
-
- Bolay H, et al. Intrinsic brain activity triggers trigeminal meningeal afferents in a migraine model. Nat Med. 2002;8:136–142. - PubMed
-
- Ophoff RA, et al. Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell. 1996;87:543–552. - PubMed
-
- Kraus RL, Sinnegger MJ, Glossmann H, Hering S, Striessnig J. Familial hemiplegic migraine mutations change α1A Ca2+ channel kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5586–5590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

