Solar-powered drip irrigation enhances food security in the Sudano-Sahel
- PMID: 20080616
- PMCID: PMC2806882
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909678107
Solar-powered drip irrigation enhances food security in the Sudano-Sahel
Abstract
Meeting the food needs of Africa's growing population over the next half-century will require technologies that significantly improve rural livelihoods at minimal environmental cost. These technologies will likely be distinct from those of the Green Revolution, which had relatively little impact in sub-Saharan Africa; consequently, few such interventions have been rigorously evaluated. This paper analyzes solar-powered drip irrigation as a strategy for enhancing food security in the rural Sudano-Sahel region of West Africa. Using a matched-pair comparison of villages in northern Benin (two treatment villages, two comparison villages), and household survey and field-level data through the first year of harvest in those villages, we find that solar-powered drip irrigation significantly augments both household income and nutritional intake, particularly during the dry season, and is cost effective compared to alternative technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
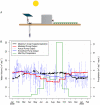

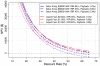
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of Food Insecurity in the World 2008: High food prices and food security—threats and opportunities. 2008.
-
- Smith LC, Alderman H, Dede A International Food Policy Research Institute. Food Insecurity in sub-Saharan Africa: New Estimates from Household Expenditure Surveys. 2006.
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations AQUASTAT—FAO’s Information System on Water and Agriculture. [Accessed July 8, 2009]. Available at: http://www.fao.org/NR/WATER/AQUASTAT/main/index.stm.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

