RBBP9: a tumor-associated serine hydrolase activity required for pancreatic neoplasia
- PMID: 20080647
- PMCID: PMC2836678
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911646107
RBBP9: a tumor-associated serine hydrolase activity required for pancreatic neoplasia
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal malignancies. To discover functionally relevant modulators of pancreatic neoplasia, we performed activity-based proteomic profiling on primary human ductal adenocarcinomas. Here, we identify retinoblastoma-binding protein 9 (RBBP9) as a tumor-associated serine hydrolase that displays elevated activity in pancreatic carcinomas. Whereas RBBP9 is expressed in normal and malignant tissues at similar levels, its elevated activity in tumor cells promotes anchorage-independent growth in vitro as well as pancreatic carcinogenesis in vivo. At the molecular level, RBBP9 activity overcomes TGF-beta-mediated antiproliferative signaling by reducing Smad2/3 phosphorylation, a previously unknown role for a serine hydrolase in cancer biology. Conversely, loss of endogenous RBBP9 or expression of mutationally inactive RBBP9 leads to elevated Smad2/3 phosphorylation, implicating this serine hydrolase as an essential suppressor of TGF-beta signaling. Finally, RBBP9-mediated suppression of TGF-beta signaling is required for E-cadherin expression as loss of the serine hydrolase activity leads to a reduction in E-cadherin levels and a concomitant decrease in the integrity of tumor cell-cell junctions. These data not only define a previously uncharacterized serine hydrolase activity associated with epithelial neoplasia, but also demonstrate the potential benefit of functional proteomics in the identification of new therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
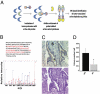
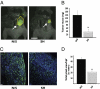
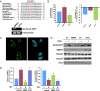
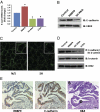
Comment in
-
Finding enzymes that are actively involved in cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 9;107(6):2379-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914955107. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133631 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chiang KP, Niessen S, Saghatelian A, Cravatt BF. An enzyme that regulates ether lipid signaling pathways in cancer annotated by multidimensional profiling. Chem Biol. 2006;13:1041–1050. - PubMed
-
- Madsen MA, Deryugina EI, Niessen S, Cravatt BF, Quigley JP. Activity-based protein profiling implicates urokinase activation as a key step in human fibrosarcoma intravasation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:15997–16005. - PubMed
-
- Jessani N, et al. A streamlined platform for high-content functional proteomics of primary human specimens. Nat Methods. 2005;2:691–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

