Dual function of CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells and conventional T cells to prevent multiorgan autoimmunity
- PMID: 20080649
- PMCID: PMC2824392
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910341107
Dual function of CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells and conventional T cells to prevent multiorgan autoimmunity
Abstract
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is an inhibitory receptor on T cells essential for maintaining T cell homeostasis and tolerance to self. Mice lacking CTLA-4 develop an early onset, fatal breakdown in T cell tolerance. Whether this autoimmune disease occurs because of the loss of CTLA-4 function in regulatory T cells, conventional T cells, or both is unclear. We show here that lack of CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells leads to aberrant activation and expansion of conventional T cells. However, CTLA-4 expression in conventional T cells prevents aberrantly activated T cells from infiltrating and fatally damaging nonlymphoid tissues. These results demonstrate that CTLA-4 has a dual function in maintaining T cell tolerance: CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells inhibits inappropriate naïve T cell activation and CTLA-4 in conventional T cells prevents the harmful accumulation of self-reactive pathogenic T cells in vital organs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


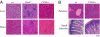
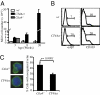
References
-
- Waterhouse P, et al. Lymphoproliferative disorders with early lethality in mice deficient in CTLA-4. Science. 1995;270:985–988. - PubMed
-
- Tivol EA, et al. Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity. 1995;3:541–547. - PubMed
-
- Chambers CA, Sullivan TJ, Allison JP. Lymphoproliferation in CTLA-4-deficient mice is mediated by costimulation-dependent activation of CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 1997;7:885–895. - PubMed
-
- Perkins D, et al. Regulation of CTLA-4 expression during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1996;156:4154–4159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

