Lipid-like materials for low-dose, in vivo gene silencing
- PMID: 20080679
- PMCID: PMC2804742
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910603106
Lipid-like materials for low-dose, in vivo gene silencing
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 25;107(21):9915
Abstract
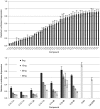
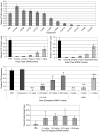
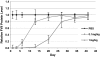
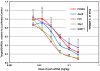
Significant effort has been applied to discover and develop vehicles which can guide small interfering RNAs (siRNA) through the many barriers guarding the interior of target cells. While studies have demonstrated the potential of gene silencing in vivo, improvements in delivery efficacy are required to fulfill the broadest potential of RNA interference therapeutics. Through the combinatorial synthesis and screening of a different class of materials, a formulation has been identified that enables siRNA-directed liver gene silencing in mice at doses below 0.01 mg/kg. This formulation was also shown to specifically inhibit expression of five hepatic genes simultaneously, after a single injection. The potential of this formulation was further validated in nonhuman primates, where high levels of knockdown of the clinically relevant gene transthyretin was observed at doses as low as 0.03 mg/kg. To our knowledge, this formulation facilitates gene silencing at orders-of-magnitude lower doses than required by any previously described siRNA liver delivery system.
Conflict of interest statement
Confllict of interest statement: The Sponsor declares a conflict of interest. R.L. is a shareholder and member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Alnylam. D.G.A. is a consultant with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. R.L and D.G.A have sponsored research grants from Alnylam. Alnylam also has a license to certain intellectual property invented at Massachusetts Institute of Technology by Drs. Anderson, Langer, and colleagues. W.Q., J.R.D., J.Q., W.C., L.L.Q., T.R., M.F.-K., K.F., V.K., A.F., R.A., D.W.Y.S., and A.A. are employed by Alnylam. The authors declare a conflict of interest. R.L. is a shareholder and member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Alnylam. D.G.A. is a consultant with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. R.L and D.G.A have sponsored research grants from Alnylam. Alnylam also has a license to certain intellectual property invented at Massachusetts Institute of Technology by Drs. Anderson, Langer, and colleagues. W.Q., J.R.D., J.Q., W.C., L.L.Q., T.R., M.F.-K., K.F., V.K., and A.A. are employed by Alnylam.
Figures


References
-
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Hall TM. Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor. Cell. 2003;115:799–811. - PubMed
-
- Judge AD, et al. Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:457–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

