Direct contacts between extracellular membrane-proximal domains are required for VEGF receptor activation and cell signaling
- PMID: 20080685
- PMCID: PMC2836632
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914052107
Direct contacts between extracellular membrane-proximal domains are required for VEGF receptor activation and cell signaling
Abstract
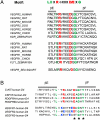
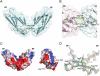
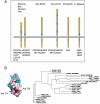
Structural analyses of the extracellular region of stem cell factor (SCF) receptor (also designated KIT) in complex with SCF revealed a sequence motif in a loop in the fourth Ig-like domain (D4) that is responsible for forming homotypic receptor contacts and for ligand-induced KIT activation and cell signaling. An identical motif was identified in the most membrane-proximal seventh Ig-like domain (D7) of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGFR2, and VEGFR3. In this report we demonstrate that ligand-induced tyrosine autophosphorylation and cell signaling via VEGFR1 or VEGFR2 harboring mutations in critical residues (Arg726 or Asp731) in D7 are strongly impaired. We also describe the crystal structure of D7 of VEGFR2 to a resolution of 2.7 A. The structure shows that homotypic D7 contacts are mediated by salt bridges and van der Waals contacts formed between Arg726 of one protomer and Asp731 of the other protomer. The structure of D7 dimer is very similar to the structure of D4 dimers seen in the crystal structure of KIT extracellular region in complex with SCF. The high similarity between VEGFR D7 and KIT D4 in both structure and function provides further evidence for common ancestral origins of type III and type V RTKs. It also reveals a conserved mechanism for RTK activation and a novel target for pharmacological intervention of pathologically activated RTKs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

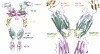
References
-
- Olsson A-K, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor signalling in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(5):359–371. - PubMed
-
- Barleon B, et al. Mapping of the sites for ligand binding and receptor dimerization at the extracellular domain of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor FLT-1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(16):10382–10388. - PubMed
-
- Shinkai A, et al. Mapping of the sites involved in ligand association and dissociation at the extracellular domain of the kinase insert domain-containing receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(47):31283–31288. - PubMed
-
- Wiesmann C, et al. Crystal structure at 1.7 A resolution of VEGF in complex with domain 2 of the Flt-1 receptor. Cell. 1997;91(5):695–704. - PubMed
-
- Shibuya M, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):549–560. (in eng) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

