Template-dependent 3'-5' nucleotide addition is a shared feature of tRNAHis guanylyltransferase enzymes from multiple domains of life
- PMID: 20080734
- PMCID: PMC2818966
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910961107
Template-dependent 3'-5' nucleotide addition is a shared feature of tRNAHis guanylyltransferase enzymes from multiple domains of life
Abstract
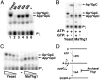
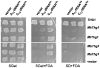
The presence of an additional 5' guanosine residue (G(-1)) is a unique feature of tRNA(His). G(-1) is incorporated posttranscriptionally in eukarya via an unusual 3'-5' nucleotide addition reaction catalyzed by the tRNA(His) guanylyltransferase (Thg1). Yeast Thg1 catalyzes an unexpected second activity: Watson-Crick-dependent 3'-5' nucleotide addition that occurs in the opposite direction to nucleotide addition by all known DNA and RNA polymerases. This discovery led to the hypothesis that there are alternative roles for Thg1 family members that take advantage of this unusual enzymatic activity. Here we show that archaeal homologs of Thg1 catalyze G(-1) addition, in vitro and in vivo in yeast, but only in a templated reaction, i.e. with tRNA(His) substrates that contain a C(73) discriminator nucleotide. Because tRNA(His) from archaea contains C(73), these findings are consistent with a physiological function for templated nucleotide addition in archaeal tRNA(His) maturation. Moreover, unlike yeast Thg1, archaeal Thg1 enzymes also exhibit a preference for template-dependent U(-1) addition to A(73)-containing tRNA(His). Taken together, these results demonstrate that Watson-Crick template-dependent 3'-5' nucleotide addition is a shared catalytic activity exhibited by Thg1 family members from multiple domains of life, and therefore, that this unusual reaction may constitute an ancestral activity present in the earliest members of the Thg1 enzyme family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


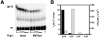
Similar articles
-
3'-5' tRNAHis guanylyltransferase in bacteria.FEBS Lett. 2010 Aug 20;584(16):3567-72. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.023. Epub 2010 Jul 23. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20650272 Free PMC article.
-
tRNAHis-guanylyltransferase establishes tRNAHis identity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(1):333-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr696. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21890903 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal requirements for reverse polymerization and tRNA repair by tRNAHis guanylyltransferase.RNA Biol. 2018;15(4-5):614-622. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1372076. Epub 2017 Sep 29. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28901837 Free PMC article.
-
Doing it in reverse: 3'-to-5' polymerization by the Thg1 superfamily.RNA. 2012 May;18(5):886-99. doi: 10.1261/rna.032300.112. Epub 2012 Mar 28. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22456265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of 3' to 5' Reverse RNA Polymerization in tRNA Fidelity and Repair.Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 26;10(3):250. doi: 10.3390/genes10030250. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30917604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3'-5' tRNAHis guanylyltransferase in bacteria.FEBS Lett. 2010 Aug 20;584(16):3567-72. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.023. Epub 2010 Jul 23. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20650272 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical 3'-5' extension of RNA with prebiotically plausible ribonucleoside 2',3'-cyclic phosphates.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Apr 9;136(14):5193-6. doi: 10.1021/ja4127714. Epub 2014 Mar 28. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24660752 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of substrate recognition and specificity of tRNAHis guanylyltransferase during nucleotide addition in the 3'-5' direction.RNA. 2018 Nov;24(11):1583-1593. doi: 10.1261/rna.067330.118. Epub 2018 Aug 15. RNA. 2018. PMID: 30111535 Free PMC article.
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Thg1 uses 5'-pyrophosphate removal to control addition of nucleotides to tRNA(His.).Biochemistry. 2014 Mar 4;53(8):1380-91. doi: 10.1021/bi4014648. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24548272 Free PMC article.
-
Functional context, biosynthesis, and genetic encoding of pyrrolysine.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011 Jun;14(3):342-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.04.001. Epub 2011 May 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21550296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosen AE, Musier-Forsyth K. Recognition of G-1:C73 atomic groups by Escherichia coli histidyl-tRNA synthetase. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(1):64–65. - PubMed
-
- Yan W, Francklyn C. Cytosine 73 is a discriminator nucleotide in vivo for histidyl-tRNA in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(13):10022–10027. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

