E3 ubiquitin ligase APC/C-Cdh1 accounts for the Warburg effect by linking glycolysis to cell proliferation
- PMID: 20080744
- PMCID: PMC2818939
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913668107
E3 ubiquitin ligase APC/C-Cdh1 accounts for the Warburg effect by linking glycolysis to cell proliferation
Abstract
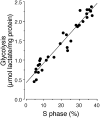
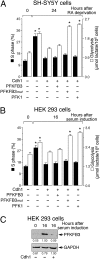
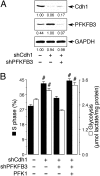
Cell proliferation is known to be accompanied by activation of glycolysis. We have recently discovered that the glycolysis-promoting enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, isoform 3 (PFKFB3), is degraded by the E3 ubiquitin ligase APC/C-Cdh1, which also degrades cell-cycle proteins. We now show in two different cell types (neoplastic and nonneoplastic) that both proliferation and aerobic glycolysis are prevented by overexpression of Cdh1 and enhanced by its silencing. Furthermore, we have coexpressed Cdh1 with PFKFB3--either wild-type or a mutant form resistant to ubiquitylation by APC/C-Cdh1--or with the glycolytic enzyme 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase and demonstrated that whereas glycolysis is essential for cell proliferation, its initiation in the presence of active Cdh1 does not result in proliferation. Our experiments indicate that the proliferative response, regardless of whether it occurs in normal or neoplastic cells, is dependent on a decrease in the activity of APC/C-Cdh1, which activates both proliferation and glycolysis. These observations have implications for cell proliferation, neoplastic transformation, and the prevention and treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

