Long-range gene regulation links genomic type 2 diabetes and obesity risk regions to HHEX, SOX4, and IRX3
- PMID: 20080751
- PMCID: PMC2818943
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911591107
Long-range gene regulation links genomic type 2 diabetes and obesity risk regions to HHEX, SOX4, and IRX3
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 8;108(10):4264
Abstract
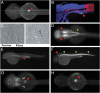
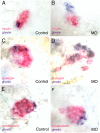
Genome-wide association studies identified noncoding SNPs associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity in linkage disequilibrium (LD) blocks encompassing HHEX-IDE and introns of CDKAL1 and FTO [Sladek R, et al. (2007) Nature 445:881-885; Steinthorsdottir V, et al. (2007) Nat. Genet 39:770-775; Frayling TM, et al. (2007) Science 316:889-894]. We show that these LD blocks contain highly conserved noncoding elements and overlap with the genomic regulatory blocks of the transcription factor genes HHEX, SOX4, and IRX3. We report that human highly conserved noncoding elements in LD with the risk SNPs drive expression in endoderm or pancreas in transgenic mice and zebrafish. Both HHEX and SOX4 have recently been implicated in pancreas development and the regulation of insulin secretion, but IRX3 had no prior association with pancreatic function or development. Knockdown of its orthologue in zebrafish, irx3a, increased the number of pancreatic ghrelin-producing epsilon cells and decreased the number of insulin-producing beta-cells and glucagon-producing alpha-cells, thereby suggesting a direct link of pancreatic IRX3 function to both obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sladek R, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;445:881–885. - PubMed
-
- Saxena R, et al. Diabetes Genetics Initiative of Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, Lund University, and Novartis Institutes of BioMedical Research. Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science. 2007;316:1331–1336. - PubMed
-
- Steinthorsdottir V, et al. A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2007;39:770–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

