Ablation of SLP-76 signaling after T cell priming generates memory CD4 T cells impaired in steady-state and cytokine-driven homeostasis
- PMID: 20080760
- PMCID: PMC2818906
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908126107
Ablation of SLP-76 signaling after T cell priming generates memory CD4 T cells impaired in steady-state and cytokine-driven homeostasis
Abstract
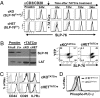
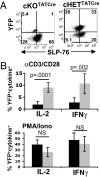
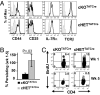
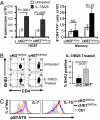
The intracellular signaling mechanisms regulating the generation and long-term persistence of memory T cells in vivo remain unclear. In this study, we used mouse models with conditional deletion of the key T cell receptor (TCR)-coupled adaptor molecule SH2-domain-containing phosphoprotein of 76 kDa (SLP-76), to analyze signaling mechanisms for memory CD4 T cell generation, maintenance, and homeostasis. We found that ablation of SLP-76 expression after T cell priming did not inhibit generation of phenotypic effector or memory CD4 T cells; however, the resultant SLP-76-deficient memory CD4 T cells could not produce recall cytokines in response to TCR-mediated stimulation and showed decreased persistence in vivo. In addition, SLP-76-deficient memory CD4 T cells exhibited reduced steady-state homeostasis and were impaired in their ability to homeostatically expand in vivo in response to the gamma(c) cytokine IL-7, despite intact proximal signaling through the IL-7R-coupled JAK3/STAT5 pathway. Direct in vivo deletion of SLP-76 in polyclonal memory CD4 T cells likewise led to impaired steady-state homeostasis as well as impaired homeostatic responses to IL-7. Our findings demonstrate a dominant role for SLP-76-dependent TCR signals in regulating turnover and perpetuation of memory CD4 T cells and their responses to homeostatic cytokines, with implications for the selective survival of memory CD4 T cells following pathogen exposure, vaccination, and aging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homeostatic division is not necessary for antigen-specific CD4+ memory T cell persistence.J Immunol. 2012 Oct 1;189(7):3378-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201583. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22956580 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired thymic selection in mice expressing altered levels of the SLP-76 adaptor protein.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Feb;83(2):419-29. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0507297. Epub 2007 Oct 26. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 17965338
-
The SLP-76 Src homology 2 domain is required for T cell development and activation.J Immunol. 2011 Nov 1;187(9):4459-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903379. Epub 2011 Sep 26. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21949020 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-driven proliferation and differentiation of human naïve, central memory and effector memory CD4+ T cells.Pathol Biol (Paris). 2003 Mar;51(2):64-6. doi: 10.1016/s0369-8114(03)00098-1. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12801802 Review.
-
T cell activation at the immunological synapse: vesicles emerge for LATer signaling.Sci Signal. 2010 May 11;3(121):pe16. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.3121pe16. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20460646 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory T cells require TCR signaling for their suppressive function.J Immunol. 2015 May 1;194(9):4362-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402384. Epub 2015 Mar 27. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25821220 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell receptor signals direct the composition and function of the memory CD8+ T-cell pool.Blood. 2010 Dec 16;116(25):5548-59. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-292748. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20847203 Free PMC article.
-
Homeostatic division is not necessary for antigen-specific CD4+ memory T cell persistence.J Immunol. 2012 Oct 1;189(7):3378-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201583. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22956580 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation of Stimulation: Cytokine Dosage and Cell Cycle Crosstalk Driving Timing-Dependent T Cell Differentiation.Front Physiol. 2018 Aug 2;9:879. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00879. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30116196 Free PMC article.
-
Human memory T cells: generation, compartmentalization and homeostasis.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Jan;14(1):24-35. doi: 10.1038/nri3567. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24336101 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reiner SL, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Division of labor with a workforce of one: Challenges in specifying effector and memory T cell fate. Science. 2007;317:622–625. - PubMed
-
- Abraham RT, Weiss A. Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MS, Singer AL, Koretzky GA. Adaptors as central mediators of signal transduction in immune cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Murali-Krishna K, et al. Persistence of memory CD8 T cells in MHC class I-deficient mice. Science. 1999;286:1377–1381. - PubMed
-
- Kassiotis G, Garcia S, Simpson E, Stockinger B. Impairment of immunological memory in the absence of MHC despite survival of memory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:244–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

