DNA aptamer-micelle as an efficient detection/delivery vehicle toward cancer cells
- PMID: 20080797
- PMCID: PMC2806697
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909611107
DNA aptamer-micelle as an efficient detection/delivery vehicle toward cancer cells
Abstract
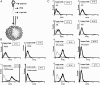
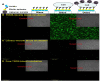
We report the design of a self-assembled aptamer-micelle nanostructure that achieves selective and strong binding of otherwise low-affinity aptamers at physiological conditions. Specific recognition ability is directly built into the nanostructures. The attachment of a lipid tail onto the end of nucleic acid aptamers provides these unique nanostructures with an internalization pathway. Other merits include: extremely low off rate once bound with target cells, rapid recognition ability with enhanced sensitivity, low critical micelle concentration values, and dual-drug delivery pathways. To prove the potential detection/delivery application of this aptamer-micelle in biological living systems, we mimicked a tumor site in the blood stream by immobilizing tumor cells onto the surface of a flow channel device. Flushing the aptamer-micelles through the channel demonstrated their selective recognition ability under flow circulation in human whole-blood sample. The aptamer-micelles show great dynamic specificity in flow channel systems that mimic drug delivery in the blood system. Therefore, our DNA aptamer-micelle assembly has shown high potential for cancer cell recognition and for in vivo drug delivery applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nucleic acid aptamers: an emerging frontier in cancer therapy.Chem Commun (Camb). 2012 Nov 4;48(85):10472-80. doi: 10.1039/c2cc35042d. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012. PMID: 22951893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-Linked Aptamer-Lipid Micelles for Excellent Stability and Specificity in Target-Cell Recognition.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Sep 3;57(36):11589-11593. doi: 10.1002/anie.201804682. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 30079455 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced targeting of 3D pancreatic cancer spheroids by aptamer-conjugated polymeric micelles with deep tumor penetration.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 5;894:173814. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173814. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33352182
-
Aptamer-based self-assembled nanomicelle enables efficient and targeted drug delivery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 9;21(1):415. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02164-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37946192 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-Functionalized Hybrid Nanostructures for Sensing, Drug Delivery, Catalysis and Mechanical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1803. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041803. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleic acid aptamers: an emerging frontier in cancer therapy.Chem Commun (Camb). 2012 Nov 4;48(85):10472-80. doi: 10.1039/c2cc35042d. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012. PMID: 22951893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-Enabled Nanomaterials for Therapeutics, Drug Targeting and Imaging.Cells. 2022 Jan 4;11(1):159. doi: 10.3390/cells11010159. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Cancer Cell-Specific Aptamers in Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Therapeutic Agents.Molecules. 2018 Apr 4;23(4):830. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040830. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29617327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trifluoromethylated Nucleic Acid Analogues Capable of Self-Assembly through Hydrophobic Interactions.Chem Sci. 2014 Oct 1;5(10):4076-4081. doi: 10.1039/C4SC01162G. Chem Sci. 2014. PMID: 25285193 Free PMC article.
-
Smart multifunctional nanostructure for targeted cancer chemotherapy and magnetic resonance imaging.ACS Nano. 2011 Oct 25;5(10):7866-73. doi: 10.1021/nn202073m. Epub 2011 Sep 21. ACS Nano. 2011. PMID: 21888350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao Q, Shi Y. Apoptosome: A platform for the activation of initiator caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:56–65. - PubMed
-
- Mikhail AS, Allen C. Block copolymer micelles for delivery of cancer therapy: Transport at the whole body, tissue and cellular levels. J Control Release. 2009;138:214–223. - PubMed
-
- Ding K, Alemdaroglu FE, Borsch M, Berger R, Herrmann A. Engineering the structural properties of DNA block copolymer micelles by molecular recognition. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46:1172–1175. - PubMed
-
- Alemdaroglu FE, Alemdaroglu NC, Langguth P, Herrmann A. Cellular uptake of DNA block copolymer micelles with different shapes. Macromolecular Rapid Communications. 2008;29:326–329.
-
- Jeong JH, Park TG. Novel polymer-DNA hybrid polymer micelles composed of hydrophobic poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) and hydrophilic oligonucleotides. Bioconjugate Chem. 2001;12:917–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

