Small RNA as global regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 20080802
- PMCID: PMC2799872
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910308106
Small RNA as global regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
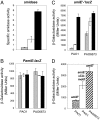
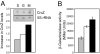
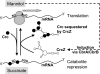
In the metabolically versatile bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the RNA-binding protein Crc is involved in catabolite repression of a range of degradative genes, such as amiE (encoding aliphatic amidase). We found that a CA-rich sequence (termed CA motif) in the amiE translation initiation region was important for Crc binding. The small RNA CrcZ (407 nt) containing 5 CA motifs was able to bind the Crc protein with high affinity and to remove it from amiE mRNA in vitro. Overexpression of crcZ relieved catabolite repression in vivo, whereas a crcZ mutation pleiotropically prevented the utilization of several carbon sources. The sigma factor RpoN and the CbrA/CbrB two-component system, which is known to maintain a healthy carbon-nitrogen balance, were necessary for crcZ expression. During growth on succinate, a preferred carbon source, CrcZ expression was low, resulting in catabolite repression of amiE and other genes under Crc control. By contrast, during growth on mannitol, a poor carbon source, elevated CrcZ levels correlated with relief of catabolite repression. During growth on glucose, an intermediate carbon source, CrcZ levels and amiE expression were intermediate between those observed in succinate and mannitol media. Thus, the CbrA-CbrB-CrcZ-Crc system allows the bacterium to adapt differentially to various carbon sources. This cascade also regulated the expression of the xylS (benR) gene, which encodes a transcriptional regulator involved in benzoate degradation, in an analogous way, confirming this cascade's global role.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Monod J. Recherches sur la croissance des cultures bactériennes. Paris: Hermann; 1942.
-
- Ullmann A. Catabolite repression: A story without end. Res Microbiol. 1996;147:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Görke B, Stülke J. Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: Many ways to make the most out of nutrients. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:613–624. - PubMed
-
- Smyth PF, Clarke PH. Catabolite repression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa amidase: The effect of carbon source on amidase synthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1975;90:81–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

