Fetal dose estimates for (18)F-fluoro-L-thymidine using a pregnant monkey model
- PMID: 20080884
- PMCID: PMC3060039
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.109.068734
Fetal dose estimates for (18)F-fluoro-L-thymidine using a pregnant monkey model
Abstract
Estimating the radiation dose received by the fetus from nuclear medicine procedures is important because of the greater sensitivity of rapidly developing fetal tissues to ionizing radiation. (18)F-fluoro-L-thymidine (FLT) uptake is related to cellular proliferation and is currently used to monitor tumor progression and response to therapy. This study was undertaken to estimate-on the basis of biodistribution data obtained by PET/CT in pregnant rhesus monkeys-radiation absorbed dose to a human fetus administered (18)F-FLT.
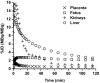
Methods: Three pregnant rhesus macaques (gestational age, 113 +/- 8 d) were administered (18)F-FLT and imaged for 2 h on a PET/CT scanner. Time-activity curves for maternal and fetal organs were generated in anatomic regions of interest identified via CT. Doses were estimated using OLINDA/EXM and the 6-mo-pregnant human model.
Results: The extrapolated whole-body maternal dose obtained, 11.4 microGy/MBq, is similar to the previously reported adult female dose of 15.6 microGy/MBq. The estimated total-body dose to a human fetus is 24 microGy/MBq. Significant long-term (18)F-FLT accumulation in fetal liver resulted in a fetal liver dose of 53 microGy/MBq.
Conclusion: The fetal dose estimate in a 6-mo-pregnant human using (18)F-FLT is slightly greater than that reported for (18)F-FDG. (18)F-FLT trapping in the fetal liver should be considered in the risk-benefit analysis of (18)F-FLT PET examination in pregnant patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fetal and maternal absorbed dose estimates for positron-emitting molecular imaging probes.J Nucl Med. 2014 Sep;55(9):1459-66. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.141309. Epub 2014 Jul 14. J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 25024424
-
Fetal Radiation Dose from 18F-FDG in Pregnant Patients Imaged with PET, PET/CT, and PET/MR.J Nucl Med. 2015 Aug;56(8):1218-22. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.157032. Epub 2015 Jun 18. J Nucl Med. 2015. PMID: 26089550
-
18F-FDG Fetal Dosimetry Calculated with PET/MRI.J Nucl Med. 2022 Oct;63(10):1592-1597. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.263561. Epub 2022 Feb 3. J Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 35115366 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation Absorbed Dose to the Embryo and Fetus from Radiopharmaceuticals.Semin Nucl Med. 2022 Mar;52(2):140-148. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2021.12.007. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Semin Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 35067360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current clinical status of 18F-FLT PET or PET/CT in digestive and abdominal organ oncology.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017 Mar;42(3):951-961. doi: 10.1007/s00261-016-0947-9. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017. PMID: 27770160 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of fetal brain uptake of paraquat in utero using in vivo PET/CT imaging.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Aug;122(2):551-6. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr104. Epub 2011 May 4. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21546347 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical PET imaging of the developing fetus during pregnancy: Current state and future potential.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 May 14:271678X251340510. doi: 10.1177/0271678X251340510. Online ahead of print. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 40367390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET/MR imaging for the evaluation of cervical cancer during pregnancy.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Apr 10;21(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-03766-w. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 33838651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vicini P, Brill AB, Stabin MG, Rescigno A. Kinetic modeling in support of radionuclide dose assessment. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38:335–346. - PubMed
-
- Stabin MG. Proposed addendum to previously published fetal dose estimate tables for 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:634–635. - PubMed
-
- Mankoff DA, Shields AF, Krohn KA. PET imaging of cellular proliferation. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;43:153–167. - PubMed
-
- Bading JR, Shields AF. Imaging of cell proliferation: status and prospects. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(suppl 2):64S–80S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
