Mouse Prkar1a haploinsufficiency leads to an increase in tumors in the Trp53+/- or Rb1+/- backgrounds and chemically induced skin papillomas by dysregulation of the cell cycle and Wnt signaling
- PMID: 20080939
- PMCID: PMC2846157
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq014
Mouse Prkar1a haploinsufficiency leads to an increase in tumors in the Trp53+/- or Rb1+/- backgrounds and chemically induced skin papillomas by dysregulation of the cell cycle and Wnt signaling
Abstract
PRKAR1A inactivation leads to dysregulated cAMP signaling and Carney complex (CNC) in humans, a syndrome associated with skin, endocrine and other tumors. The CNC phenotype is not easily explained by the ubiquitous cAMP signaling defect; furthermore, Prkar1a(+/-) mice did not develop skin and other CNC tumors. To identify whether a Prkar1a defect is truly a generic but weak tumorigenic signal that depends on tissue-specific or other factors, we investigated Prkar1a(+/-) mice when bred within the Rb1(+/-) or Trp53(+/-) backgrounds, or treated with a two-step skin carcinogenesis protocol. Prkar1a(+/-) Trp53(+/-) mice developed more sarcomas than Trp53(+/-) mice (P < 0.05) and Prkar1a(+/-) Rb1(+/-) mice grew more (and larger) pituitary and thyroid tumors than Rb1(+/-) mice. All mice with double heterozygosity had significantly reduced life-spans compared with their single-heterozygous counterparts. Prkar1a(+/-) mice also developed more papillomas than wild-type animals. A whole-genome transcriptome profiling of tumors produced by all three models identified Wnt signaling as the main pathway activated by abnormal cAMP signaling, along with cell cycle abnormalities; all changes were confirmed by qRT-PCR array and immunohistochemistry. siRNA down-regulation of Ctnnb1, E2f1 or Cdk4 inhibited proliferation of human adrenal cells bearing a PRKAR1A-inactivating mutation and Prkar1a(+/-) mouse embryonic fibroblasts and arrested both cell lines at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. In conclusion, Prkar1a haploinsufficiency is a relatively weak tumorigenic signal that can act synergistically with other tumor suppressor gene defects or chemicals to induce tumors, mostly through Wnt-signaling activation and cell cycle dysregulation, consistent with studies in human neoplasms carrying PRKAR1A defects.
Figures


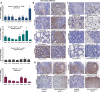
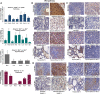
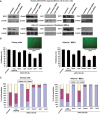

References
-
- Carney J.A., Gordon H., Carpenter P.C., Shenoy B.V., Go V.L. The complex of myxomas, spotty pigmentation, and endocrine overactivity. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985;64:270–283. - PubMed
-
- Stratakis C.A., Kirschner L.S., Carney J.A. Clinical and molecular features of the Carney complex: diagnostic criteria and recommendations for patient evaluation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;86:4041–4046. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner L.S., Carney J.A., Pack S.D., Taymans S.E., Giatzakis C., Cho Y.S., Cho-Chung Y.S., Stratakis C.A. Mutations of the gene encoding the protein kinase A type I-alpha regulatory subunit in patients with the Carney complex. Nat. Genet. 2000;26:89–92. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner L.S., Sandrini F., Monbo J., Lin J.P., Carney J.A., Stratakis C.A. Genetic heterogeneity and spectrum of mutations of the PRKAR1A gene in patients with the carney complex. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000;9:3037–3046. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner L.S., Kusewitt D.F., Matyakhina L., Towns W.H., 2nd, Carney J.A., Westphal H., Stratakis C.A. A mouse model for the Carney complex tumor syndrome develops neoplasia in cyclic AMP-responsive tissues. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4506–4514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

