Role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in metabolic regulation by JNK1
- PMID: 20080940
- PMCID: PMC2811827
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1878510
Role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in metabolic regulation by JNK1
Abstract
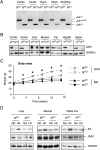
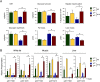
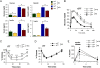
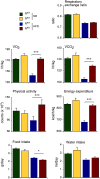
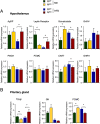
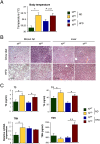
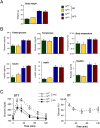
The cJun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) is implicated in diet-induced obesity. Indeed, germline ablation of the murine Jnk1 gene prevents diet-induced obesity. Here we demonstrate that selective deficiency of JNK1 in the murine nervous system is sufficient to suppress diet-induced obesity. The failure to increase body mass is mediated, in part, by increased energy expenditure that is associated with activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Disruption of thyroid hormone function prevents the effects of nervous system JNK1 deficiency on body mass. These data demonstrate that the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis represents an important target of metabolic signaling by JNK1.
Figures
References
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF. The c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307) J Biol Chem. 2000;275:9047–9054. - PubMed
-
- Bennett BL, Satoh Y, Lewis AJ. JNK: A new therapeutic target for diabetes. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003;3:420–425. - PubMed
-
- Björkman U, Ekholm R. Biochemistry of thyroid hormone formation and secretion. In: Greer MA, editor. The thyroid gland. Raven Press; New York: 2000. pp. 83–125.
-
- Dong C, Yang DD, Wysk M, Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ, Flavell RA. Defective T cell differentiation in the absence of Jnk1. Science. 1998;282:2092–2095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
