Decylubiquinone increases mitochondrial function in synaptosomes
- PMID: 20080966
- PMCID: PMC2838286
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.079780
Decylubiquinone increases mitochondrial function in synaptosomes
Abstract
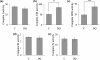
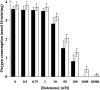
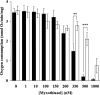
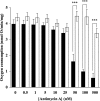
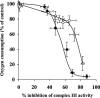
The effects of decylubiquinone, a ubiquinone analogue, on mitochondrial function and inhibition thresholds of the electron transport chain enzyme complexes in synaptosomes were investigated. Decylubiquinone increased complex I/III and complex II/III activities by 64 and 80%, respectively, and attenuated reductions in oxygen consumption at high concentrations of the complex III inhibitor myxothiazol. During inhibition of complex I, decylubiquinone attenuated reductions in synaptosomal oxygen respiration rates, as seen in the complex I inhibition threshold. Decylubiquinone increased the inhibition thresholds of complex I/III, complex II/III, and complex III over oxygen consumption in the nerve terminal by 25-50%, when myxothiazol was used to inhibit complex III. These results imply that decylubiquinone increases mitochondrial function in the nerve terminal during complex I or III inhibition. The potential benefits of decylubiquinone in diseases where complex I, I/III, II/III, or III activities are deficient are discussed.
Figures
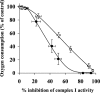
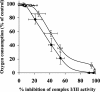
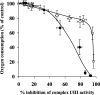
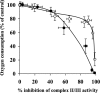
References
-
- Cleren C., Yang L., Lorenzo B., Calingasan N. Y., Schomer A., Sireci A., Wille E. J., Beal M. F. (2008) J. Neurochem. 104, 1613–1621 - PubMed
-
- Beal M. F., Matthews R. T., Tieleman A., Shults C. W. (1998) Brain Res. 783, 109–114 - PubMed
-
- Moon Y., Lee K. H., Park J. H., Geum D., Kim K. (2005) J. Neurochem. 93, 1199–1208 - PubMed
-
- Smith K. M., Matson S., Matson W. R., Cormier K., Del Signore S. J., Hagerty S. W., Stack E. C., Ryu H., Ferrante R. J. (2006) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1762, 616–626 - PubMed
-
- Shults C. W. (2005) Pharmacol. Ther. 107, 120–130 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

