Prolactin enhances insulin-like growth factor I receptor phosphorylation by decreasing its association with the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20080972
- PMCID: PMC2832951
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066480
Prolactin enhances insulin-like growth factor I receptor phosphorylation by decreasing its association with the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Abstract
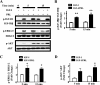
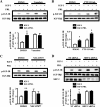
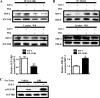
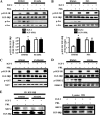
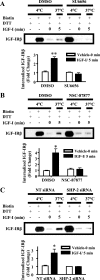
Normal mammary development requires coordinated interactions of numerous factors, including prolactin (PRL) and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), both of which have also been implicated in breast cancer pathogenesis and progression. We previously reported that PRL and IGF-I synergize in breast cancer cells to activate ERK1/2 and AKT, leading to increased proliferation, survival, and invasion. Intriguingly, PRL co-treatment with IGF-I augments IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) phosphorylation 2-fold higher than IGF-I alone. Here, we showed the importance of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in this cross-talk using pharmacological inhibition and small interfering RNA. SHP-2 recruitment to IGF-IR was significantly attenuated by PRL co-treatment. Src family kinase activity was required for IGF-IR association with SHP-2, ligand-induced IGF-IR internalization, and PRL-enhanced IGF-IR phosphorylation. Inhibition of internalization, via knockdown of the GTPase, dynamin-2, prevented not only IGF-IR dephosphorylation, but also PRL-enhanced IGF-IR phosphorylation. Consistently, PRL diminished IGF-I-induced IGF-IR internalization, which may result from reduced SHP-2 association with IGF-IR, because we demonstrated an essential role for SHP-2 in IGF-IR internalization. Together, these findings describe a novel mechanism of cross-talk between PRL and IGF-I in breast cancer cells, with implications for our understanding of tumor progression and potential therapeutic strategies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):15682-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092270. Epub 2010 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20207740 Free PMC article.
-
p66shc negatively regulates insulin-like growth factor I signal transduction via inhibition of p52shc binding to Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 leading to impaired growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 membrane recruitment.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Sep;22(9):2162-75. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0079. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18606861 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I receptor dephosphorylation by SHPS-1 and the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2.J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 15;277(11):8955-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109258200. Epub 2002 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11779860
-
Role of estrogen receptor alpha in modulating IGF-I receptor signaling and function in breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep;23(3):385-94. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15595626 Review.
-
Interaction between insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and alphaVbeta3 integrin linked signaling pathways: cellular responses to changes in multiple signaling inputs.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jan;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0376. Epub 2004 Nov 4. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15528274 Review.
Cited by
-
Src kinases in chondrosarcoma chemoresistance and migration: dasatinib sensitises to doxorubicin in TP53 mutant cells.Br J Cancer. 2013 Sep 3;109(5):1214-22. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.451. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23922104 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin activates ERα in the absence of ligand in female mammary development and carcinogenesis in vivo.Endocrinology. 2013 Dec;154(12):4483-92. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1533. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 24064365 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and saturable nature of signaling pathways induced by metreleptin in humans: comparative evaluation of in vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro administration.Diabetes. 2015 Mar;64(3):828-39. doi: 10.2337/db14-0625. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25249580 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A review of Dynamin 2 involvement in cancers highlights a promising therapeutic target.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jul 22;40(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02045-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34294140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unexploited therapies in breast and prostate cancer: blockade of the prolactin receptor.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Nov;21(11):691-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20846877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

