The receiver domain of hybrid histidine kinase VirA: an enhancing factor for vir gene expression in Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- PMID: 20081031
- PMCID: PMC2832513
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01007-09
The receiver domain of hybrid histidine kinase VirA: an enhancing factor for vir gene expression in Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Abstract
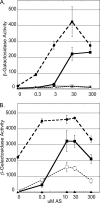
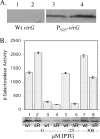
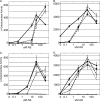
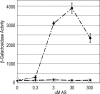
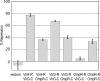
The plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens expresses virulence (vir) genes in response to chemical signals found at the site of a plant wound. VirA, a hybrid histidine kinase, and its cognate response regulator, VirG, regulate vir gene expression. The receiver domain at the carboxyl end of VirA has been described as an inhibitory element because its removal increased vir gene expression relative to that of full-length VirA. However, experiments that characterized the receiver region as an inhibitory element were performed in the presence of constitutively expressed virG. We show here that VirA's receiver domain is an activating factor if virG is expressed from its native promoter on the Ti plasmid. When virADeltaR was expressed from a multicopy plasmid, both sugar and the phenolic inducer were essential for vir gene expression. Replacement of wild-type virA on pTi with virADeltaR precluded vir gene induction, and the cells did not accumulate VirG or induce transcription of a virG-lacZ fusion in response to acetosyringone. These phenotypes were corrected if the virG copy number was increased. In addition, we show that the VirA receiver domain can interact with the VirG DNA-binding domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reconstitution of acetosyringone-mediated Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence gene expression in the heterologous host Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jun;183(12):3704-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.12.3704-3711.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11371534 Free PMC article.
-
Mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virG gene that activate transcription of vir promoter in Escherichia coli.Curr Microbiol. 2004 Nov;49(5):334-40. doi: 10.1007/s00284-004-4359-7. Curr Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15486707
-
Efficient vir gene induction in Agrobacterium tumefaciens requires virA, virG, and vir box from the same Ti plasmid.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jul;183(13):4079-89. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.13.4079-4089.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11395473 Free PMC article.
-
The sensing of plant signal molecules by Agrobacterium: genetic evidence for direct recognition of phenolic inducers by the VirA protein.Gene. 1996 Nov 7;179(1):83-8. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00328-9. Gene. 1996. PMID: 8955632 Review.
-
Agrobacterium virulence gene induction.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;343:77-84. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-130-4:77. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16988335 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering robust control of two-component system phosphotransfer using modular scaffolds.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 30;109(44):18090-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209230109. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23071327 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Analysis of the VirA Sensor Kinase in Agrobacterium tumefaciens Using Structural Models.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 16;13:898785. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.898785. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35651496 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphate flow between hybrid histidine kinases CheA₃ and CheS₃ controls Rhodospirillum centenum cyst formation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1004002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004002. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367276 Free PMC article.
-
Agrobacterium tumefaciens responses to plant-derived signaling molecules.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jul 8;5:322. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00322. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25071805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the VirA histidine autokinase of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in the initial steps of pathogenesis.Front Plant Sci. 2014 May 14;5:195. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00195. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24860585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1992. Short protocols in molecular biology, 2nd ed. John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY.
-
- Baikalov, I., I. Schroder, M. Kaczor-Grzeskowiak, K. Grzeskowiak, R. P. Gunsalus, and R. E. Dickerson. 1996. Structure of the Escherichia coli regulator NarL. Biochemistry 34:11053-11061. - PubMed
-
- Brencic, A., Q. Xia, and S. C. Winans. 2004. VirA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is an intradimer transphosphorylase and can actively block vir gene expression in the absence of phenolic signals. Mol. Microbiol. 52:1349-1362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

