L718P mutation in the membrane-proximal cytoplasmic tail of beta 3 promotes abnormal alpha IIb beta 3 clustering and lipid microdomain coalescence, and associates with a thrombasthenia-like phenotype
- PMID: 20081061
- PMCID: PMC2895041
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.018572
L718P mutation in the membrane-proximal cytoplasmic tail of beta 3 promotes abnormal alpha IIb beta 3 clustering and lipid microdomain coalescence, and associates with a thrombasthenia-like phenotype
Abstract
Background: Support for the role of transmembrane and membrane-proximal domains of alpha IIb beta 3 integrin in the maintenance of receptor low affinity comes from mutational studies showing that activating mutations can induce constitutive bi-directional transmembrane signaling.
Design and methods: We report the functional characterization of a mutant alpha IIb beta 3 integrin carrying the Leu718Pro mutation in the membrane-proximal region of the beta 3 cytoplasmic domain, identified in heterozygosis in a patient with a severe bleeding phenotype and defective platelet aggregation and adhesion.
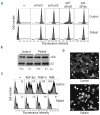
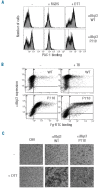
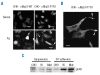
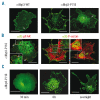
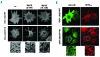
Results: Transiently transfected cells expressed similar levels of normal and mutant alpha IIb beta 3, but surface expression of mutant alpha v beta 3 was reduced due to its retention in intracellular compartments. Cells stably expressing mutant alpha IIb beta 3 showed constitutive binding to soluble multivalent ligands as well as spontaneous fibrinogen-dependent aggregation, but their response to DTT was markedly reduced. Fibrinogen-adherent cells exhibited a peculiar spreading phenotype with long protrusions. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed the formation of alpha IIb beta 3 clusters underneath the entire cell body and the presence of atypical high-density patches of clustered alpha IIb beta 3 containing encircled areas devoid of integrin that showed decreased affinity for the fluorescent lipid analog DiIC(16) and were disrupted in cholesterol-depleted cells.
Conclusions: These findings are consistent with an important role of the membrane-proximal region of beta 3 in modulating alpha IIb beta 3 clustering and lateral redistribution of membrane lipids. Since the beta 3 mutant was associated with a thrombasthenic phenotype in a patient carrying one normal beta 3 allele, these results support a dominant role of clustering in regulating integrin alpha IIb beta 3 functions in vivo.
Figures
Comment in
-
Regulation of platelet beta 3 integrins.Haematologica. 2010 Jul;95(7):1049-51. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.024893. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20595101 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110(6):673–87. - PubMed
-
- Partridge AW, Liu S, Kim S, Bowie JU, Ginsberg MH. Transmembrane domain helix packing stabilizes integrin αIIbβ3 in the low affinity state. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(8):7294–300. - PubMed
-
- Hughes P, O’Toole TE, Ylänne J, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH. The conserved membrane-proximal region of an integrin cytoplasmic domain specifies ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(21):12411–7. - PubMed
-
- Ma YQ, Yang J, Pesho MM, Vinogradova O, Qin J, Plow EF. Regulation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation by distinct regions of its cytoplasmic tails. Biochemistry. 2006;45(21):6656–62. - PubMed

