Composite functional genetic and comedication CYP2D6 activity score in predicting tamoxifen drug exposure among breast cancer patients
- PMID: 20081063
- PMCID: PMC3816977
- DOI: 10.1177/0091270009359182
Composite functional genetic and comedication CYP2D6 activity score in predicting tamoxifen drug exposure among breast cancer patients
Erratum in
- J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;50(6):725. Philip, Santosh [corrected to Philips, Sanosh]
Abstract
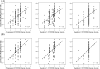
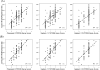
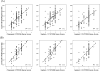
Accurate assessment of CYP2D6 phenotypes from genotype is inadequate in patients taking CYP2D6 substrate together with CYP2D6 inhibitors. A novel CYP2D6 scoring system is proposed that incorporates the impact of concomitant medications with the genotype in calculating the CYP2D6 activity score. Training (n = 159) and validation (n = 81) data sets were obtained from a prospective cohort tamoxifen pharmacogenetics registry. Two inhibitor factors were defined: 1 genotype independent and 1 genotype based. Three CYP2D6 gene scoring systems, and their combination with the inhibitor factors, were compared. These 3 scores were based on Zineh, Zanger, and Gaedigk's approaches. Endoxifen/NDM-Tam plasma ratio was used as the phenotype. The overall performance of the 3 gene scoring systems without consideration of CYP2D6-inhibiting medications in predicting CYP2D6 phenotype was poor in both the training set (R(2) = 0.24, 0.22, and 0.18) and the validation set (R(2) = 0.30, 0.24, and 0.15). Once the CYP2D6 genotype-independent inhibitor factor was integrated into the score calculation, the R(2) values in the training and validation data sets were nearly twice as high as the genotype-only scoring model: (0.44, 0.43, 0.38) and (0.53, 0.50, 0.41), respectively. The integration of the inhibitory effect of concomitant medications with the CYP2D6 genotype into the composite CYP2D6 activity score doubled the ability to predict the CYP2D6 phenotype. However, endoxifen phenotypes still varied substantially, even with incorporation of CYD2D6 genotype and inhibiting factors, suggesting that other, as yet unidentified factors must be involved in tamoxifen activation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pharmacogenetic-based clinical scores: a useful, simple tool to predict tamoxifen-based CYP2D6 phenotype?J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;50(4):370-2. doi: 10.1177/0091270009353605. Epub 2010 Jan 20. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20089828 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ingelman-Sundberg M, Johansson I, Persson I, Oscarson M, Hu Y, Bertilsson L, et al. Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450. Functional consequences and possible relationship to disease and alcohol toxicity. EXS. 1994;71:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Ingelman-Sundberg M. Pharmacogenetics of cytochrome P450 and its applications in drug therapy: the past, present and future. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Desta Z, Ward BA, Soukhova NV, Flockhart DA. Comprehensive evaluation of tamoxifen sequential biotransformation by the human cytochrome P450 system in vitro: prominent roles for CYP3A and CYP2D6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;310:1062–75. - PubMed
-
- Tyndale RF, Droll KP, Sellers EM. Genetically deficient CYP2D6 metabolism provides protection against oral opiate dependence. Pharmacogenetics. 1997;7:375–9. - PubMed
-
- Dahl ML, Johansson I, Palmertz MP, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Sjoqvist F. Analysis of the CYP2D6 gene in relation to debrisoquin and desipramine hydroxylation in a Swedish population. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992;51:12–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM088076/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 2U-01 GM61373/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM74217/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008425/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32-GM-08425/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061373/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074217/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24RR020815/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR020815/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States