Pax6-dependent Shroom3 expression regulates apical constriction during lens placode invagination
- PMID: 20081189
- PMCID: PMC2858910
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.045369
Pax6-dependent Shroom3 expression regulates apical constriction during lens placode invagination
Abstract
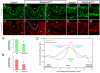
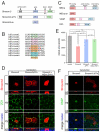
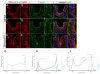
Embryonic development requires a complex series of relative cellular movements and shape changes that are generally referred to as morphogenesis. Although some of the mechanisms underlying morphogenesis have been identified, the process is still poorly understood. Here, we address mechanisms of epithelial morphogenesis using the vertebrate lens as a model system. We show that the apical constriction of lens epithelial cells that accompanies invagination of the lens placode is dependent on Shroom3, a molecule previously associated with apical constriction during morphogenesis of the neural plate. We show that Shroom3 is required for the apical localization of F-actin and myosin II, both crucial components of the contractile complexes required for apical constriction, and for the apical localization of Vasp, a Mena family protein with F-actin anti-capping function that is also required for morphogenesis. Finally, we show that the expression of Shroom3 is dependent on the crucial lens-induction transcription factor Pax6. This provides a previously missing link between lens-induction pathways and the morphogenesis machinery and partly explains the absence of lens morphogenesis in Pax6-deficient mutants.
Figures




Similar articles
-
p120-catenin-dependent junctional recruitment of Shroom3 is required for apical constriction during lens pit morphogenesis.Development. 2014 Aug;141(16):3177-87. doi: 10.1242/dev.107433. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Development. 2014. PMID: 25038041 Free PMC article.
-
A Trio-RhoA-Shroom3 pathway is required for apical constriction and epithelial invagination.Development. 2011 Dec;138(23):5177-88. doi: 10.1242/dev.067868. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Development. 2011. PMID: 22031541 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-dependent modes of Pax6-Sox2 epistasis regulate lens development and eye morphogenesis.Development. 2009 Sep;136(17):2977-85. doi: 10.1242/dev.037341. Development. 2009. PMID: 19666824 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6: a multi-level regulator of ocular development.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012 Sep;31(5):351-76. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 May 3. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22561546 Review.
-
Role of a transcription factor Pax6 in the developing vertebrate olfactory system.Dev Growth Differ. 2007 Dec;49(9):683-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2007.00965.x. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Dev Growth Differ. 2007. PMID: 17908181 Review.
Cited by
-
A possible connection between reactive oxygen species and the unfolded protein response in lens development: From insight to foresight.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 21;10:820949. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.820949. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36211466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of gene expression in microarrays and expressed sequence tags from normal and cataractous lenses.Hum Genomics. 2012 Sep 1;6(1):14. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-6-14. Hum Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23244575 Free PMC article.
-
Making a head: Neural crest and ectodermal placodes in cranial sensory development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 30;138:15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.06.009. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35760729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cellular and molecular mechanisms of vertebrate lens development.Development. 2014 Dec;141(23):4432-47. doi: 10.1242/dev.107953. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Development. 2014. PMID: 25406393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lens actin filament cytoskeleton: Diverse structures for complex functions.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Mar;156:58-71. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 26971460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altmann C. R., Chow, R. L., Lang, R. A. and Hemmati-Brivanlou, A. (1997). Lens induction by Pax-6 in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Biol. 185, 119-123. - PubMed
-
- Ball L. J., Kuhne, R., Hoffmann, B., Hafner, A., Schmieder, P., Volkmer-Engert, R., Hof, M., Wahl, M., Schneider-Mergener, J., Walter, U., et al. (2000). Dual epitope recognition by the VASP EVH1 domain modulates polyproline ligand specificity and binding affinity. EMBO J. 19, 4903-4914. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ball L. J., Jarchau, T., Oschkinat, H. and Walter, U. (2002). EVH1 domains: structure, function and interactions. FEBS Lett. 513, 45-52. - PubMed
-
- Barrett K., Leptin, M. and Settleman, J. (1997). The Rho GTPase and a putative RhoGEF mediate a signaling pathway for the cell shape changes in Drosophila gastrulation. Cell 91, 905-915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

