NUDT16 and ITPA play a dual protective role in maintaining chromosome stability and cell growth by eliminating dIDP/IDP and dITP/ITP from nucleotide pools in mammals
- PMID: 20081199
- PMCID: PMC2875033
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1250
NUDT16 and ITPA play a dual protective role in maintaining chromosome stability and cell growth by eliminating dIDP/IDP and dITP/ITP from nucleotide pools in mammals
Abstract
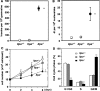
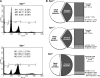
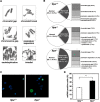
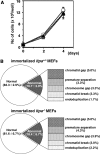
Mammalian inosine triphosphatase encoded by ITPA gene hydrolyzes ITP and dITP to monophosphates, avoiding their deleterious effects. Itpa(-) mice exhibited perinatal lethality, and significantly higher levels of inosine in cellular RNA and deoxyinosine in nuclear DNA were detected in Itpa(-) embryos than in wild-type embryos. Therefore, we examined the effects of ITPA deficiency on mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Itpa(-) primary MEFs lacking ITP-hydrolyzing activity exhibited a prolonged doubling time, increased chromosome abnormalities and accumulation of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA, compared with primary MEFs prepared from wild-type embryos. However, immortalized Itpa(-) MEFs had neither of these phenotypes and had a significantly higher ITP/IDP-hydrolyzing activity than Itpa(-) embryos or primary MEFs. Mammalian NUDT16 proteins exhibit strong dIDP/IDP-hydrolyzing activity and similarly low levels of Nudt16 mRNA and protein were detected in primary MEFs derived from both wild-type and Itpa(-) embryos. However, immortalized Itpa(-) MEFs expressed significantly higher levels of Nudt16 than the wild type. Moreover, introduction of silencing RNAs against Nudt16 into immortalized Itpa(-) MEFs reproduced ITPA-deficient phenotypes. We thus conclude that NUDT16 and ITPA play a dual protective role for eliminating dIDP/IDP and dITP/ITP from nucleotide pools in mammals.
Figures
References
-
- Nakabeppu Y, Tsuchimoto D, Furuichi M, Sakumi K. The defense mechanisms in mammalian cells against oxidative damage in nucleic acids and their involvement in the suppression of mutagenesis and cell death. Free Radic. Res. 2004;38:423–429. - PubMed
-
- Nakabeppu Y, Behmanesh M, Yamaguchi H, Yoshimura D, Sakumi K. In: Oxidative Damage to Nucleic Acids. Evans MD, Cooke MS, editors. TX/New York: Landes Bioscience/Springer, Austin; 2007. pp. 40–53.
-
- Nakabeppu Y. Molecular genetics and structural biology of human MutT homolog, MTH1. Mutat. Res. 2001;477:59–70. - PubMed
-
- Nakabeppu Y, Kajitani K, Sakamoto K, Yamaguchi H, Tsuchimoto D. MTH1, an oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphatase, prevents the cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity of oxidized purine nucleotides. DNA Rep. 2006;5:761–772. - PubMed
-
- Behmanesh M, Sakumi K, Tsuchimoto D, Torisu K, Ohnishi-Honda Y, Rancourt DE, Nakabeppu Y. Characterization of the structure and expression of mouse Itpa gene and its related sequences in the mouse genome. DNA Res. 2005;12:39–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

