Artery-to-vein differences in nitric oxide metabolites are diminished in sepsis
- PMID: 20081526
- PMCID: PMC3322374
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181d16a3e
Artery-to-vein differences in nitric oxide metabolites are diminished in sepsis
Abstract
Objective: Nitric oxide deficiency may contribute to microvascular dysfunction in sepsis. Current physiologic paradigms contend that nitrite and/or S-nitrosohemoglobin mediate intravascular delivery of nitric oxide. These nitric oxide metabolites are purportedly consumed during hemoglobin deoxygenation, producing nitric oxide and coupling intravascular nitric oxide delivery with metabolic demand. Systemic nitrite and S-nitrosohemoglobin consumption can be assessed by comparing their concentrations in arterial vs. venous blood. We hypothesized that arterial vs. venous differences in nitrite and S-nitrosohemoglobin are diminished in sepsis and associated with mortality.
Design: Case-control and prospective cohort study.
Setting: Adult intensive care units of an academic medical center.
Patients and subjects: Eighty-seven critically ill septic patients and 52 control subjects.
Interventions: None.
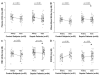
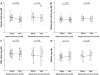
Measurements and main results: Nitrite and S-nitrosohemoglobin were measured using tri-iodide-based reductive chemiluminescence. In control subjects, arterial plasma, whole blood, and red blood cell nitrite levels were higher than the corresponding venous levels. In contrast, S-nitrosohemoglobin was higher in venous compared to arterial blood. In septic patients, arterial vs. venous red blood cell nitrite and S-nitrosohemoglobin differences were absent. Furthermore, the plasma nitrite arterial vs. venous difference was absent in nonsurvivors.
Conclusions: In health, nitrite levels are higher in arterial vs. venous blood (suggesting systemic nitrite consumption), whereas S-nitrosohemoglobin levels are higher in venous vs. arterial blood (suggesting systemic S-nitrosohemoglobin production). These arterial vs. venous differences are diminished in sepsis, and diminished arterial vs. venous plasma nitrite differences are associated with mortality. These data suggest pathologic disruption of systemic nitrite utilization in sepsis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reduced arteriovenous nitrite gradients associated with sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2010 Apr;38(4):1214-5. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cfb3fd. Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20335702 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Reduced arteriovenous nitrite gradients associated with sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2010 Apr;38(4):1214-5. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cfb3fd. Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20335702 No abstract available.
-
Nitrite and S-Nitrosohemoglobin Exchange Across the Human Cerebral and Femoral Circulation: Relationship to Basal and Exercise Blood Flow Responses to Hypoxia.Circulation. 2017 Jan 10;135(2):166-176. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024226. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 27881556 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of circulating nitrite and S-nitrosohemoglobin in the regulation of regional blood flow in humans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11482-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.21.11482. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11027349 Free PMC article.
-
S-nitrosohemoglobin: a biochemical perspective.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 Apr 15;36(8):947-58. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.01.008. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15059635 Review.
-
Nitric oxide, S-nitrosothiols and hemoglobin: is methodology the key?Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Jun;25(6):311-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2004.04.009. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15165746 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioavailable estradiol concentrations are elevated and predict mortality in septic patients: a prospective cohort study.Crit Care. 2016 Oct 21;20(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1525-9. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27765072 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic High-Altitude Hypoxia Alters Iron and Nitric Oxide Homeostasis in Fetal and Maternal Sheep Blood and Aorta.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;11(9):1821. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091821. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139895 Free PMC article.
-
Brachial artery reactivity in patients with severe sepsis: an observational study.Crit Care. 2012 Dec 12;16(2):R38. doi: 10.1186/cc11223. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22390813 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of T- and R-state stabilization on deoxyhemoglobin-nitrite reactions and stimulation of nitric oxide signaling.Nitric Oxide. 2011 Aug 1;25(2):59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Nitric Oxide. 2011. PMID: 21277987 Free PMC article.
-
Microcirculation dysfunction in endotoxic shock rabbits is associated with impaired S-nitrosohemoglobin-mediated nitric oxide release from red blood cells: a preliminary study.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019 Jan 7;7(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40635-018-0215-0. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019. PMID: 30617929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landry D, Oliver JA. The pathogenesis of vasodilatory shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:588–595. - PubMed
-
- Trzeciak S, Cinel I, Dellinger P, Shapiro NI, Arnold RC, Parrillo JE, Hollenberg SM, on behalf of the Microcirculatory Alterations in Resuscitation and Shock (MARS) Investigators Resuscitating the microcirculation in sepsis: The central role of nitric oxide, emerging concepts for novel therapies, and challenges for clinical trials. Acad Emerg Med. 2008;15:399–413. - PMC - PubMed
-
- MacKanzie I, Garrard CS, Young JD. Indices of nitric oxide synthesis and outcome in critically ill patients. Anaesthesia. 2001;56:326–330. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Jimenez J, Salgado A, Mourelle M, Cruz Martin M, Segura RM, Peracaula R, Moncada S. L-arginine: Nitric oxide pathway in endotoxemia and human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:253–258. - PubMed
-
- Evans T, Carpenter A, Kinderman H, Cohen J. Evidence of increased nitric oxide production in patients with the sepsis syndrome. Circ Shock. 1993;41:77–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

