Mechanistic insights into a Ca2+-dependent family of alpha-mannosidases in a human gut symbiont
- PMID: 20081828
- PMCID: PMC3942423
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.278
Mechanistic insights into a Ca2+-dependent family of alpha-mannosidases in a human gut symbiont
Abstract
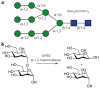
Colonic bacteria, exemplified by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, play a key role in maintaining human health by harnessing large families of glycoside hydrolases (GHs) to exploit dietary polysaccharides and host glycans as nutrients. Such GH family expansion is exemplified by the 23 family GH92 glycosidases encoded by the B. thetaiotaomicron genome. Here we show that these are alpha-mannosidases that act via a single displacement mechanism to utilize host N-glycans. The three-dimensional structure of two GH92 mannosidases defines a family of two-domain proteins in which the catalytic center is located at the domain interface, providing acid (glutamate) and base (aspartate) assistance to hydrolysis in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. The three-dimensional structures of the GH92s in complex with inhibitors provide insight into the specificity, mechanism and conformational itinerary of catalysis. Ca(2+) plays a key catalytic role in helping distort the mannoside away from its ground-state (4)C(1) chair conformation toward the transition state.
Figures


References
-
- Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell. 2006;124:837–848. - PubMed
-
- Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science. 2005;307:1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Turnbaugh PJ, et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006;444:1027–1031. - PubMed
-
- Mazmanian SK, Round JL, Kasper DL. A microbial symbiosis factor prevents intestinal inflammatory disease. Nature. 2008;453:620–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- BB/G016127/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK075322/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BB/E000568/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- P41 GM103390/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR005351/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

