New genetic loci implicated in fasting glucose homeostasis and their impact on type 2 diabetes risk
- PMID: 20081858
- PMCID: PMC3018764
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.520
New genetic loci implicated in fasting glucose homeostasis and their impact on type 2 diabetes risk
Erratum in
- Nat Genet.2010 May;42(5):464
Abstract
Levels of circulating glucose are tightly regulated. To identify new loci influencing glycemic traits, we performed meta-analyses of 21 genome-wide association studies informative for fasting glucose, fasting insulin and indices of beta-cell function (HOMA-B) and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in up to 46,186 nondiabetic participants. Follow-up of 25 loci in up to 76,558 additional subjects identified 16 loci associated with fasting glucose and HOMA-B and two loci associated with fasting insulin and HOMA-IR. These include nine loci newly associated with fasting glucose (in or near ADCY5, MADD, ADRA2A, CRY2, FADS1, GLIS3, SLC2A2, PROX1 and C2CD4B) and one influencing fasting insulin and HOMA-IR (near IGF1). We also demonstrated association of ADCY5, PROX1, GCK, GCKR and DGKB-TMEM195 with type 2 diabetes. Within these loci, likely biological candidate genes influence signal transduction, cell proliferation, development, glucose-sensing and circadian regulation. Our results demonstrate that genetic studies of glycemic traits can identify type 2 diabetes risk loci, as well as loci containing gene variants that are associated with a modest elevation in glucose levels but are not associated with overt diabetes.
Figures
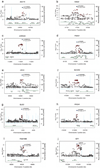
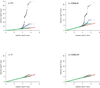
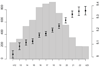
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus: Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:3160–3167. - PubMed
-
- Coutinho M, Gerstein HC, Wang Y, Yusuf S. The relationship between glucose and incident cardiovascular events. A metaregression analysis of published data from 20 studies of 95,783 individuals followed for 12.4 years. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:233–240. - PubMed
-
- Meigs JB, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB, Sr, Wilson PW. Fasting and postchallenge glycemia and cardiovascular disease risk: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1845–1850. - PubMed
-
- UKPDS. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33) Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560–2572. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0801056/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600331/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G19/35/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 077011/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK029867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 091746/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 089061/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U127592696/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/07/008/23674/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A620_1015/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0100222/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 088885/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0700222(81696)/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G8802774/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0902037/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686857/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 077016/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0700222/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 064890/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0600717/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 081682/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R69/0208/DMT_/The Dunhill Medical Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

