AHI1 is required for photoreceptor outer segment development and is a modifier for retinal degeneration in nephronophthisis
- PMID: 20081859
- PMCID: PMC2884967
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.519
AHI1 is required for photoreceptor outer segment development and is a modifier for retinal degeneration in nephronophthisis
Abstract
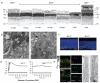
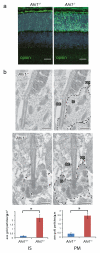
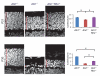
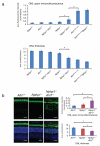
Degeneration of photoreceptors is a common feature of ciliopathies, owing to the importance of the specialized ciliary structure of these cells. Mutations in AHI1, which encodes a cilium-localized protein, have been shown to cause a form of Joubert syndrome that is highly penetrant for retinal degeneration. We show that Ahi1-null mice fail to form retinal outer segments and have abnormal distribution of opsin throughout their photoreceptors. Apoptotic cell death of photoreceptors occurs rapidly between 2 and 4 weeks of age in these mice and is significantly (P = 0.00175 and 0.00613) delayed by a reduced dosage of opsin. This phenotype also shows dosage-sensitive genetic interactions with Nphp1, another ciliopathy-related gene. Although it is not a primary cause of retinal blindness in humans, we show that an allele of AHI1 is associated with a more than sevenfold increase in relative risk of retinal degeneration within a cohort of individuals with the hereditary kidney disease nephronophthisis. Our data support context-specific roles for AHI1 as a contributor to retinopathy and show that AHI1 may explain a proportion of the variability in retinal phenotypes observed in nephronophthisis.
Figures
References
-
- Valente EM, et al. AHI1 gene mutations cause specific forms of Joubert syndrome-related disorders. Ann Neurol. 2006;59:527–34. - PubMed
-
- Quinlan RJ, Tobin JL, Beales PL. Modeling ciliopathies: Primary cilia in development and disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;84:249–310. - PubMed
-
- Ferland RJ, et al. Abnormal cerebellar development and axonal decussation due to mutations in AHI1 in Joubert syndrome. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1008–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31NS059281/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY007042/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY007042/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GGP08145/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- T32 GM008666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS059281/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013408/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

