Borders, extent, and topography of human perirhinal cortex as revealed using multiple modern neuroanatomical and pathological markers
- PMID: 20082329
- PMCID: PMC6870967
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20940
Borders, extent, and topography of human perirhinal cortex as revealed using multiple modern neuroanatomical and pathological markers
Abstract
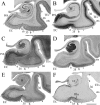
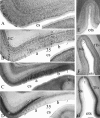
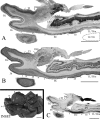
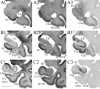
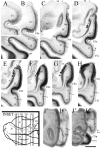
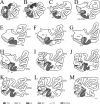
Despite rapidly increasing interests in specific contributions of different components of human medial temporal lobe (MTL) to memory and memory impairments in normal aging and in many abnormal conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and Pick's disease, few modern neuroanatomical studies are available about the borders, extent, and topography of human perirhinal areas 35 and 36, which are important components of the MTL memory system. By a combined use of several cellular, neurochemical, and pathological markers, which mainly include neuronal nuclear antigen, calcium-binding proteins (parvalbumin and calbindin-D28k), nonphosphorylated neurofilament protein (SMI-32), Wisteria floribunda agglutinin, and abnormally phosphorylated tau (AT8), this study has revealed that the borders of human perirhinal areas 35 and 36 are significantly different from those defined with conventional Nissl staining. In general, areas 35 and 36 occupy the ventromedial temporopolar and rhinal sulcal regions, the collateral sulcal region, and the anterior two-thirds of fusiform gyrus or occipitotemporal gyrus. Furthermore, the precise borders, extent, and topography of human areas 35 and 36 and adjoining entorhinal cortex were marked at different anteroposterior levels of the MTL with reference to variations of rhinal and collateral sulci and other useful landmarks. These findings would provide reliable neuroanatomical base for the great and yet rapidly increasing number of neuroimaging studies of the human MTL structures in healthy and many abnormal conditions.
Hum Brain Mapp, 2010. © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Arnold SE ( 2000): Cellular and molecular neuropathology of the parahippocampal region in schizophrenia. Ann NY Acad Sci 911: 275–292. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SE,Hyman BT,Flory J,Damasio AR,Van Hoesen GW ( 1991): The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Cereb Cortex 1: 103–116. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi N,Bernasconi A,Caramanos Z,Andermann F,Dubeau F,Arnold DL ( 2000): Morphometric MRI analysis of the parahippocampal region in temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann NY Acad Sci 911: 495–500. - PubMed
-
- Blatt GJ,Rosene DL ( 1998): Organization of direct hippocampal efferent projections to the cerebral cortex of the rhesus monkey: Projections from CA1, prosubiculum, and subiculum to the temporal lobe. J Comp Neurol 392: 92–114. - PubMed
-
- Blatt GJ,Pandya DN,Rosene DL ( 2003): Parcellation of cortical afferents to three distinct sectors in the parahippocampal gyrus of the rhesus monkey: An anatomical and neurophysiological study. J Comp Neurol 466: 161–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

