Acute hypoxia modifies cAMP levels induced by inhibitors of phosphodiesterase-4 in rat carotid bodies, carotid arteries and superior cervical ganglia
- PMID: 20082613
- PMCID: PMC2825357
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00534.x
Acute hypoxia modifies cAMP levels induced by inhibitors of phosphodiesterase-4 in rat carotid bodies, carotid arteries and superior cervical ganglia
Abstract
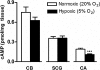
Background and purpose: Phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors are useful to treat hypoxia-related diseases and are used in experiments studying the effects of oxygen on 3'-5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production. We studied the effects of acute hypoxia on cAMP accumulation induced by PDE inhibitors in oxygen-specific chemosensors, the carotid bodies (CBs) and in non-chemosensitive CB-related structures: carotid arteries (CAs) and superior cervical ganglia (SCG).
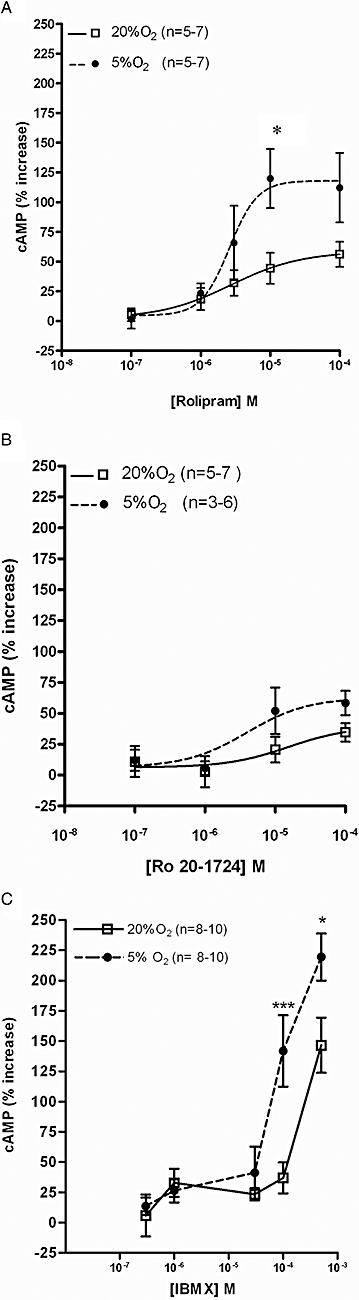
Experimental approach: Concentration-response curves for the effects of a non-specific PDE inhibitor [isobutylmethylxanthine (IBMX) ], PDE4 selective inhibitors (rolipram, Ro 20-1724) and a PDE2 selective inhibitor (erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine) on cAMP levels were obtained in normoxic (20% O(2)/5% CO(2)) or hypoxic (5% O(2)/5% CO(2)) conditions.
Key results: Responses to the PDE inhibitors were compatible with the presence of PDE4 in rat CBs, CAs and SCG but in the absence of PDE2 in CAs and CBs. Acute hypoxia enhanced the effects of IBMX and PDE4 inhibitors on cAMP accumulation in CAs and CBs. In SCG, acute hypoxia reduced cAMP accumulation induced by all the four PDE inhibitors tested. Differences between the effects of Ro 20-1724 and rolipram on cAMP were found in CAs and CBs during hypoxia.
Conclusions and implications: The effects of PDE4 inhibitors could be potentiated or inhibited by acute hypoxia depending on the PDE isoforms of the tissue. The similarities between the characterization of PDE4 inhibitors at the CBs and CAs, under normoxia and hypoxia, did not support a specific role for cAMP in the oxygen-sensing machinery at the CB and suggested that no direct CB-mediated, hyperventilatory, adverse effects would be expected with administration of PDE4 inhibitors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of phosphodiesterases 4 in the rat carotid body: effect of oxygen concentrations.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;648:113-9. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-2259-2_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19536472
-
Species differences in behavioural effects of rolipram and other adenosine cyclic 3H, 5H-monophosphate phosphodiesterase inhibitors.J Neural Transm. 1983;56(2-3):139-52. doi: 10.1007/BF01243273. J Neural Transm. 1983. PMID: 6190991
-
Effects of a cardiotonic quinolinone derivative Y-20487 on the isoproterenol-induced positive inotropic action and cyclic AMP accumulation in rat ventricular myocardium: comparison with rolipram, Ro 20-1724, milrinone, and isobutylmethylxanthine.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;20(5):715-22. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1280732
-
PET measurements of cAMP-mediated phosphodiesterase-4 with (R)-[11C]rolipram.Curr Radiopharm. 2011 Jan;4(1):44-58. doi: 10.2174/1874471011104010044. Curr Radiopharm. 2011. PMID: 22191614 Review.
-
Neurotensin receptor 1 immunoreactivity in the peripheral ganglia and carotid body.Eur J Histochem. 2009 Sep 23;53(3):e16. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2009.e16. Eur J Histochem. 2009. PMID: 19864207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lessons from single-cell transcriptome analysis of oxygen-sensing cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 May;372(2):403-415. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2682-0. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 28887696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Cervical Sympathetic Chain Input to the Superior Cervical Ganglia Affects the Ventilatory Responses to Hypoxic Challenge in Freely-Moving C57BL6 Mice.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 22;12:619688. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.619688. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33967819 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oxygen on phosphodiesterases (PDE) 3 and 4 isoforms and PKA activity in the superior cervical ganglia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;758:287-94. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4584-1_39. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23080174 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous sulfur dioxide is a novel inhibitor of hypoxia-induced mast cell degranulation.J Adv Res. 2020 Sep 8;29:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.08.017. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 33842005 Free PMC article.
-
β-Adrenoceptor blockade prevents carotid body hyperactivity and elevated vascular sympathetic nerve density induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Jan;473(1):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02492-0. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33210151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal RP, Spector T, Parks RE. Tight-binding inhibitors-IV. Inhibition of adenosine deaminases by various inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;26:359–367. - PubMed
-
- Almaraz L, Perez-Garcia MT, Gonzalez C. Presence of D1 receptors in the rabbit carotid body. Neurosci Lett. 1991;132(2):259–262. - PubMed
-
- Batuca JR, Monteiro TC, Monteiro EC. Contribution of dopamine D2 receptors for the cAMP levels at the carotid body. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;536:367–373. - PubMed
-
- Bender AT, Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:488–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

