Upstream stimulating factors 1 and 2 enhance transcription from the placenta-specific promoter 1.1 of the bovine cyp19 gene
- PMID: 20082704
- PMCID: PMC2822775
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-5
Upstream stimulating factors 1 and 2 enhance transcription from the placenta-specific promoter 1.1 of the bovine cyp19 gene
Abstract
Background: Placenta-derived oestrogens have an impact on the growth and differentiation of the trophoblast, and are involved in processes initiating and facilitating birth. The enzyme that converts androgens into oestrogens, aromatase cytochrome P450 (P450arom), is encoded by the Cyp19 gene. In the placenta of the cow, expression of Cyp19 relies on promoter 1.1 (P1.1). Our recent studies of P1.1 in vitro and in a human trophoblast cell line (Jeg3) revealed that interactions of placental nuclear protein(s) with the E-box element at position -340 are required for full promoter activity. The aim of this work was to identify and characterise the placental E-box (-340)-binding protein(s) (E-BP) as a step towards understanding how the expression of Cyp19 is regulated in the bovine placenta.
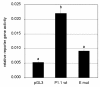
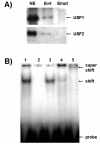
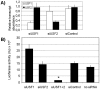
Results: The significance of the E-box was confirmed in cultured primary bovine trophoblasts. We enriched the E-BP from placental nuclear extracts using DNA-affinity Dynabeads and showed by Western blot analysis and supershift EMSA experiments that the E-BP is composed of the transcription factors upstream stimulating factor (USF) 1 and USF2. Depletion of the USFs by RNAi and expression of a dominant-negative USF mutant, were both associated with a significant decrease in P1.1-dependent reporter gene expression. Furthermore, scatter plot analysis of P1.1 activity vs. USF binding to the E-box revealed a strong positive correlation between the two parameters.
Conclusion: From these results we conclude that USF1 and USF2 are activators of the bovine placenta-specific promoter P1.1 and thus act in the opposite mode as in the case of the non-orthologous human placenta-specific promoter.
Figures
Similar articles
-
USF1 and USF2 mediate inhibition of human trophoblast differentiation and CYP19 gene expression by Mash-2 and hypoxia.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Sep;23(17):6117-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.17.6117-6128.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12917334 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the regulatory regions of the human aromatase (P450arom) gene involved in placenta-specific expression.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;12(11):1764-77. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.11.0190. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9817601
-
Identification of the core promoter of ZNFO, an oocyte-specific maternal effect gene in cattle.Gene. 2021 Jul 30;791:145717. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145717. Epub 2021 May 13. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33991649
-
Mechanisms in the regulation of aromatase in developing ovary and placenta.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Aug-Sep;106(1-5):62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.05.001. Epub 2007 May 21. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17596931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of transcriptional regulatory elements of the human aromatase cytochrome P450 gene (CYP19).J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):151-9. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00232-4. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603036 Review.
Cited by
-
The basic helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper transcription factor USF2 integrates serum-induced PAI-1 expression and keratinocyte growth.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Oct;115(10):1840-7. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24861. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24905330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang WC, Nakao T, Moriyoshi M, Nakada K, Ohtaki T, Ribadu AY, Tanaka Y. The relationship between plasma oestrone sulphate concentrations in pregnant dairy cattle and calf birth weight, calf viability, placental weight and placental expulsion. Anim Reprod Sci. 1999;54:169–178. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4320(98)00154-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

