Truncating mutations in the Wilson disease gene ATP7B are associated with very low serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activity and an early onset of Wilson disease
- PMID: 20082719
- PMCID: PMC2845088
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-8
Truncating mutations in the Wilson disease gene ATP7B are associated with very low serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activity and an early onset of Wilson disease
Abstract
Background: Mutations in the gene ATP7B cause Wilson disease, a copper storage disorder with a high phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity. We aimed to evaluate whether 'severe' protein-truncating ATP7B mutations (SMs) are associated with low serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activities and an early age of onset when compared to missense mutations (MMs).
Methods: The clinical phenotype of 59 genetically confirmed WD patients was analyzed retrospectively. Serum ceruloplasmin was measured by its oxidase activity with o-dianisidine dihydrochloride as substrate and immunologically.
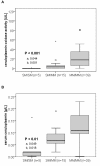
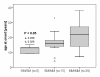
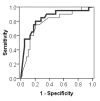
Results: Thirty-nine patients had two MMs, 15 had the genotype SM/MM, and 5 patients had two SMs on their ATP7B alleles. Enzymatic and immunologic serum ceruloplasmin levels differed significantly between the three groups (P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively). The lowest levels were measured in patients with two SMs (0.0 U/L; IQR, 0.0-0.0 U/L and 0.02 g/L; IQR, 0.01-0.02 g/L, respectively) and the highest in patients with two MMs (17.8 U/L; IQR, 5.8-35.1 U/L and 0.11 g/L; IQR,0.10-0.17 g/L, respectively). The age of onset was also significantly different between the three patient groups (P < 0.05), with SM/SM patients showing the earliest onset (13 years; IQR, 9-13 years) and patients with two MMs showing the latest onset (22 years; IQR, 14-27 years). By ROC curve analysis a ceruloplasmin oxidase level <or= 5 U/L can predict the presence of at least one SM with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 79.5%.
Conclusions: In our German study cohort truncating ATP7B mutations were associated with lower ceruloplasmin serum oxidase levels and an earlier age of onset when compared to MMs. Measurement of serum ceruloplasmin oxidase might help to predict presence of truncating ATP7B mutations and might facilitate the mutation analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of ATP7B mutation detection rate with biochemical characteristics in Korean patients with Wilson disease.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2010 Winter;40(1):15-9. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2010. PMID: 20124325
-
Frameshift and nonsense mutations in the gene for ATPase7B are associated with severe impairment of copper metabolism and with an early clinical manifestation of Wilson's disease.Clin Genet. 2005 Dec;68(6):524-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2005.00528.x. Clin Genet. 2005. PMID: 16283883
-
Evidence for a critical role of ceruloplasmin oxidase activity in iron metabolism of Wilson disease gene knockout mice.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jun;25(6):1144-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06173.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20594231
-
Wilson disease.Med Electron Microsc. 2002 Jun;35(2):61-6. doi: 10.1007/s007950200007. Med Electron Microsc. 2002. PMID: 12181646 Review.
-
Copper transporting P-type ATPases and human disease.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2002 Oct;34(5):333-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1021293818125. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2002. PMID: 12539960 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Forensic Signs Resulting from Exposure to Heavy Metals and Other Chemical Elements of the Periodic Table.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 29;12(7):2591. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072591. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the diagnostic value of serum ceruloplasmin for Wilson's disease in children.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Mar 16;22(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02186-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35296237 Free PMC article.
-
Management Perspective of Wilson's Disease: Early Diagnosis and Individualized Therapy.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(4):465-485. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200429233517. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32351182 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of two novel mutations in the ATP7B gene that cause Wilson's disease.World J Pediatr. 2017 Aug;13(4):387-391. doi: 10.1007/s12519-017-0055-0. Epub 2017 Aug 15. World J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28856630
-
Wilson disease: At the crossroads between genetics and epigenetics-A review of the evidence.Liver Res. 2017 Sep;1(2):121-130. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Liver Res. 2017. PMID: 29270329 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

