Phenotypic plasticity in development and evolution: facts and concepts. Introduction
- PMID: 20083631
- PMCID: PMC2817147
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0267
Phenotypic plasticity in development and evolution: facts and concepts. Introduction
Abstract
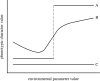
This theme issue pursues an exploration of the potential of taking into account the environmental sensitivity of development to explaining the evolution of metazoan life cycles, with special focus on complex life cycles and the role of developmental plasticity. The evolution of switches between alternative phenotypes as a response to different environmental cues and the evolution of the control of the temporal expression of alternative phenotypes within an organism's life cycle are here treated together as different dimensions of the complex relationships between genotype and phenotype, fostering the emergence of a more general and comprehensive picture of phenotypic evolution through a quite diverse sample of case studies. This introductory article reviews fundamental facts and concepts about phenotypic plasticity, adopting the most authoritative terminology in use in the current literature. The main topics are types and components of phenotypic variation, the evolution of organismal traits through plasticity, the origin and evolution of phenotypic plasticity and its adaptive value.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental plasticity and the evolution of animal complex life cycles.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010 Feb 27;365(1540):631-40. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0268. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20083638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a population genetic framework of developmental evolution: the costs, limits, and consequences of phenotypic plasticity.Bioessays. 2010 Jan;32(1):71-81. doi: 10.1002/bies.200900132. Bioessays. 2010. PMID: 20020499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution and molecular mechanisms of adaptive developmental plasticity.Mol Ecol. 2011 Apr;20(7):1347-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05016.x. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Mol Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21342300 Review.
-
Using phenotypic plasticity to understand the structure and evolution of the genotype-phenotype map.Genetica. 2022 Aug;150(3-4):209-221. doi: 10.1007/s10709-021-00135-5. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Genetica. 2022. PMID: 34617196 Review.
-
Hormones and phenotypic plasticity in an ecological context: linking physiological mechanisms to evolutionary processes.Integr Comp Biol. 2014 Nov;54(5):850-63. doi: 10.1093/icb/icu019. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Integr Comp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24752548
Cited by
-
Genetic growth potential, rather than phenotypic size, predicts migration phenotype in Atlantic salmon.Proc Biol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;287(1931):20200867. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2020.0867. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Proc Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32693717 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-dependent expression of sperm genes in ADL chemosensory neurons is required for olfactory responses in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jul 11;11:1396587. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1396587. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39055986 Free PMC article.
-
The plasticity of the grapevine berry transcriptome.Genome Biol. 2013 Jun 7;14(6):r54. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-r54. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 23759170 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic regulatory strategies of crabs: the transition from water to land.Front Physiol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1399194. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1399194. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39397859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatially and Temporally Distributed Complexity-A Refreshed Framework for the Study of GRN Evolution.Cells. 2022 May 30;11(11):1790. doi: 10.3390/cells11111790. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberch P.1991From genes to phenotype: dynamical systems and evolvability. Genetica 84, 5–11 (doi:10.1007/BF00123979) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Applebaum S. W., Heifetz Y.1999Density-dependent physiological phase in insects. Ann. Rev. Ent. 44, 317–341 (doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.44.1.317) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arenas-Mena C.2010Indirect development, transdifferentiation and the macroregulatory evolution of metazoans. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 365, 653–669 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0253) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldwin J. M.1896A new factor in evolution. Am. Nat. 30, 441–451, 536–553 (doi:10.1086/276408) - DOI
-
- Braendle C., Flatt T.2006A role for genetic accommodation in evolution? Bioessays 28, 868–873 (doi:10.1002/bies.20456) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

