Concentration-dependent noncysteinyl leukotriene type 1 receptor-mediated inhibitory activity of leukotriene receptor antagonists
- PMID: 20083671
- PMCID: PMC2826199
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900071
Concentration-dependent noncysteinyl leukotriene type 1 receptor-mediated inhibitory activity of leukotriene receptor antagonists
Abstract
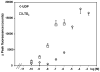
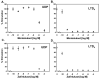
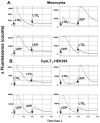
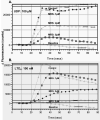
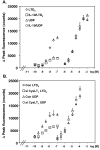
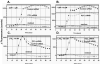
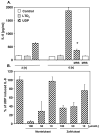
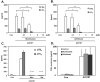
The use of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) for asthma therapy has been associated with a significant degree of interpatient variability in response to treatment. Some of that variability may be attributable to noncysteinyl leukotriene type 1 receptor (CysLT(1))-mediated inhibitory mechanisms that have been demonstrated for this group of drugs. We used a model of CysLT(1) signaling in human monocytes to characterize CysLT(1)-dependent and -independent anti-inflammatory activity of two chemically different, clinically relevant LTRAs (montelukast and zafirlukast). Using receptor-desensitization experiments in monocytes and CysLT(1)-transfected HEK293 cells and IL-10- and CysLT(1) small interfering RNA-induced downregulation of CysLT(1) expression, we showed that reported CysLT(1) agonists leukotriene D(4) and UDP signal through calcium mobilization, acting on separate receptors, and that both pathways were inhibited by montelukast and zafirlukast. However, 3-log greater concentrations of LTRAs were required for the inhibition of UDP-induced signaling. In monocytes, UDP, but not leukotriene D(4), induced IL-8 production that was significantly inhibited by both drugs at micromolar concentrations. At low micromolar concentrations, both LTRAs also inhibited calcium ionophore-induced leukotriene (leukotriene B(4) and leukotriene C(4)) production, indicating 5-lipoxygenase inhibitory activities. We report herein that montelukast and zafirlukast, acting in a concentration-dependent manner, can inhibit non-CysLT(1)-mediated proinflammatory reactions, suggesting activities potentially relevant for interpatient variability in response to treatment. Higher doses of currently known LTRAs or new compounds derived from this class of drugs may represent a new strategy for finding more efficient therapy for bronchial asthma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Inhibit Mitogenic Activity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Mar 27;19(3):833-837. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.3.833. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29582642 Free PMC article.
-
Differential inhibitory effects of CysLT(1) receptor antagonists on P2Y(6) receptor-mediated signaling and ion transport in human bronchial epithelia.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022363. Epub 2011 Jul 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21799837 Free PMC article.
-
Inverse agonist activity of selected ligands of the cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 1.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Apr;309(1):102-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.059824. Epub 2004 Jan 12. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 14718577
-
Neuromodulatory effects of leukotriene receptor antagonists: A comprehensive review.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 5;978:176755. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176755. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38909933 Review.
-
Pharmacology of leukotriene receptor antagonists.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Jun;157(6 Pt 2):S214-8; discussion S218-9, S247-8. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. PMID: 9647602 Review.
Cited by
-
Cooperative and redundant signaling of leukotriene B4 and leukotriene D4 in human monocytes.Allergy. 2011 Oct;66(10):1304-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02647.x. Epub 2011 May 24. Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21605126 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-1 antagonists as modulators of innate immune cell function.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:608930. doi: 10.1155/2014/608930. Epub 2014 May 25. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24971371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Inhibit Migration, Invasion, and Expression of MMP-2/9 in Human Glioblastoma.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;38(2):559-573. doi: 10.1007/s10571-017-0507-z. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28600709 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules as Toll-like Receptor 4 Modulators Drug and In-House Computational Repurposing.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 19;10(9):2326. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092326. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140427 Free PMC article.
-
The complex pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis: scientific rationale for the development of an alternative treatment option.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019 Apr 16;15:24. doi: 10.1186/s13223-018-0314-1. eCollection 2019. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31015846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Spector SL, Smith LJ, Glass M. Effects of 6 weeks of therapy with oral doses of ICI 204,219, a leukotriene D4 receptor antagonist, in subjects with bronchial asthma. ACCOLATE Asthma Trialists Group. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994;150:618–623. - PubMed
-
- Reiss TF, Chervinsky P, Dockhorn RJ, Shingo S, Seidenberg B, Edwards TB. Montelukast, a once-daily leukotriene receptor antagonist, in the treatment of chronic asthma: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial. Montelukast Clinical Research Study Group. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998;158:1213–1220. - PubMed
-
- Malmstrom K, Rodriguez-Gomez G, Guerra J, Villaran C, Pineiro A, Wei LX, Seidenberg BC, Reiss TF. Oral montelukast, inhaled beclomethasone, and placebo for chronic asthma. A randomized, controlled trial. Montelukast/Beclomethasone Study Group. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999;130:487–495. - PubMed
-
- Szefler SJ, Phillips BR, Martinez FD, Chinchilli VM, Lemanske RF, Strunk RC, Zeiger RS, Larsen G, Spahn JD, Bacharier LB, Bloomberg GR, Guilbert TW, Heldt G, Morgan WJ, Moss MH, Sorkness CA, Taussig LM. Characterization of within-subject responses to fluticasone and montelukast in childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;115:233–242. - PubMed
-
- In KH, Asano K, Beier D, Grobholz J, Finn PW, Silverman EK, Silverman ES, Collins T, Fischer AR, Keith TP, Serino K, Kim SW, De Sanctis GT, Yandava C, Pillari A, Rubin P, Kemp J, Israel E, Busse W, Ledford D, Murray JJ, Segal A, Tinkleman D, Drazen JM. Naturally occurring mutations in the human 5-lipoxygenase gene promoter that modify transcription factor binding and reporter gene transcription. J. Clin. Invest. 1997;99:1130–1137. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

