T cell/transmembrane, Ig, and mucin-3 allelic variants differentially recognize phosphatidylserine and mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells
- PMID: 20083673
- PMCID: PMC3128800
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903059
T cell/transmembrane, Ig, and mucin-3 allelic variants differentially recognize phosphatidylserine and mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells
Abstract
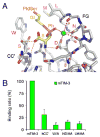
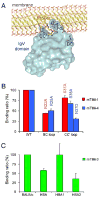
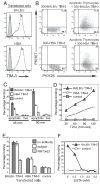
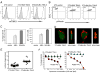
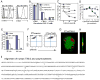
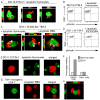
T cell/transmembrane, Ig, and mucin (TIM) proteins, identified using a congenic mouse model of asthma, critically regulate innate and adaptive immunity. TIM-1 and TIM-4 are receptors for phosphatidylserine (PtdSer), exposed on the surfaces of apoptotic cells. Herein, we show with structural and biological studies that TIM-3 is also a receptor for PtdSer that binds in a pocket on the N-terminal IgV domain in coordination with a calcium ion. The TIM-3/PtdSer structure is similar to that of TIM-4/PtdSer, reflecting a conserved PtdSer binding mode by TIM family members. Fibroblastic cells expressing mouse or human TIM-3 bound and phagocytosed apoptotic cells, with the BALB/c allelic variant of mouse TIM-3 showing a higher capacity than the congenic C.D2 Es-Hba-allelic variant. These functional differences were due to structural differences in the BC loop of the IgV domain of the TIM-3 polymorphic variants. In contrast to fibroblastic cells, T or B cells expressing TIM-3 formed conjugates with but failed to engulf apoptotic cells. Together these findings indicate that TIM-3-expressing cells can respond to apoptotic cells, but the consequence of TIM-3 engagement of PtdSer depends on the polymorphic variants of and type of cell expressing TIM-3. These findings establish a new paradigm for TIM proteins as PtdSer receptors and unify the function of the TIM gene family, which has been associated with asthma and autoimmunity and shown to modulate peripheral tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
TIM genes: a family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity.Immunol Rev. 2010 May;235(1):172-89. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00903.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20536563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Human and Murine T-Cell Immunoglobulin Mucin Domain 4 (TIM-4) IgV Domain Residues Critical for Ebola Virus Entry.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):6097-6111. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00100-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27122575 Free PMC article.
-
TIM-1 and TIM-4 glycoproteins bind phosphatidylserine and mediate uptake of apoptotic cells.Immunity. 2007 Dec;27(6):927-40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.011. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 18082433 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing functional domains for TIM-mediated enveloped virus entry.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(12):6702-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00300-14. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24696470 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of phosphatidylserine exposed on the viral envelope and cell membrane in HIV-1 replication.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Oct 21;17(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0452-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31638994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis A Virus Cellular Receptor 1 (HAVcr-1) Initiates Prostate Cancer Progression in Human Cells via Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF)-Induced Changes in Junctional Integrity.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 21;12(2):338. doi: 10.3390/biom12020338. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204839 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory receptors and ligands beyond PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4: breakthroughs or backups.Nat Immunol. 2019 Nov;20(11):1425-1434. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0512-0. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31611702 Review.
-
The mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor mediates plasminogen-induced efferocytosis.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Mar;105(3):519-530. doi: 10.1002/JLB.1AB0417-160RR. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30657605 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Tim-3 in Cancer With Resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 22;11:731175. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.731175. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34631560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Trafficking of Cell Surface and Endosomal TIM-1 to the Immune Synapse.Traffic. 2015 Nov;16(11):1193-207. doi: 10.1111/tra.12329. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 26332704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McIntire JJ, Umetsu SE, Akbari O, Potter M, Kuchroo VK, Barsh GS, Freeman GJ, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH. Identification of Tapr (an airway hyperreactivity regulatory locus) and the linked Tim gene family. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:1109–1116. - PubMed
-
- Kuchroo VK, Umetsu DT, DeKruyff RH, Freeman GJ. The TIM gene family: emerging roles in immunity and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:454–462. - PubMed
-
- McIntire JJ, Umetsu SE, Macaubas C, Hoyte EG, Cinnioglu C, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Barsh GS, Hallmayer JF, Underhill PA, Risch NJ, et al. Immunology: hepatitis A virus link to atopic disease. Nature. 2003;425:576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

