Nimodipine and acceleration of functional recovery of the facial nerve after crush injury
- PMID: 20083741
- PMCID: PMC4394364
- DOI: 10.1001/archfacial.2009.95
Nimodipine and acceleration of functional recovery of the facial nerve after crush injury
Abstract
Objective: To establish whether nimodipine, a calcium channel blocker, accelerates or otherwise improves functional recovery of whisking after facial nerve crush injury in the rat.
Methods: Thirty rats underwent exposure of the left main trunk of the facial nerve followed by a standard crush injury and subsequent quantitative facial movement testing. Animals were randomized into an experimental group (n = 15) and a control group (n = 15). Four days prior to facial nerve manipulation, experimental animals underwent subcutaneous implantation of a nimodipine-secreting pellet. All animals were tested preoperatively and on postoperative days 2, 8 to 17, 20, 22, 24, and 31 using a validated, quantitative whisking kinematics apparatus. Whisks were analyzed for amplitude, velocity, and acceleration.
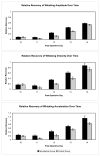
Results: Animals receiving nimodipine demonstrated significantly better whisking on 5 days (postoperative days 9, 11 to 13, and 20) compared with control animals (P < .001, P = .003, P = .009, P = .009, and P = .009, respectively; 1-tailed ttest). Overall, the nimodipine-treated animals showed earlier recovery compared with the untreated animals.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that nimodipine improves recovery of whisking after facial nerve crush. This finding corroborates the semiquantitative findings of others, and provides complete whisking kinematic data on its effects. Given the low adverse effect profile of nimodipine, there may be clinical implications in its administration in patients experiencing facial nerve injury.
Figures

References
-
- Yeh C, Bowers D, Hadlock TA. Effect of FK506 on functional recovery after facial nerve injury in the rat. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2007;9:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Ito M, Ohbayashi M, Furukawa M, Okoyama S. Neuroprotective effects of TJ-23 (Tokishakuyakusan) on adult rat motoneurons following peripheral facial nerve axotomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;136:225–230. - PubMed
-
- Reinecke K, Lucius R, Reinecke A, Rickert U, Herdegen T, Unger T. Angiotensin II accelerates functional recovery in the rat sciatic nerve in vivo: role of the AT2 receptor and the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Faseb J. 2003;17:2094–2096. - PubMed
-
- Hindley S, Juurlink BH, Gysbers JW, Middlemiss PJ, Herman MA, Rathbone MP. Nitric oxide donors enhance neurotrophin-induced neurite outgrowth through a cGMP-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci Res. 1997;47:427–439. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Hernandez T, Rustioni A. Nitric oxide synthase and growth-associated protein are coexpressed in primary sensory neurons after peripheral injury. J Comp Neurol. 1999;404:64–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
