Oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer disease in the frontal cortex
- PMID: 20084018
- PMCID: PMC2826839
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181cb5af4
Oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer disease in the frontal cortex
Abstract
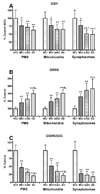
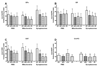
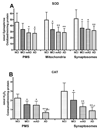
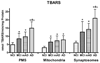
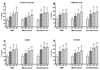
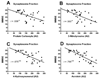
We investigated oxidative stress in human postmortem frontal cortexfrom individuals characterized as mild cognitive impairment (n= 8), mild/moderate Alzheimer disease (n = 4), and late-stage Alzheimer disease (n = 9). Samples from subjects with no cognitive impairment (n = 10) that were age- and postmortem interval-matched with these cases were used as controls. The short postmortem intervalbrain samples were processed for postmitochondrial supernatant, nonsynaptic mitochondria, and synaptosome fractions. Samples were analyzed for several antioxidants (glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, glutathione-S-transferase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, superoxide dismutase, catalase) and the oxidative marker, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. The tissue was also analyzed for possible changes in protein damage using neurochemical markers for protein carbonyls, 3-nitrotyrosine, 4-hydroxynonenal, andacrolein. All 3 neuropil fractions (postmitochondrial supernatant, mitochondrial, and synaptosomal) demonstrated significant disease-dependent increases in oxidative markers. The highest changes were observed in the synaptosomal fraction. Both mitochondrial and synaptosomal fractions had significant declines in antioxidants (glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, and superoxide dismutase). Levels of oxidative markers significantly correlated with Mini-Mental Status Examination scores. Oxidative stress was more localized to the synapses, with levels increasing in a disease-dependent fashion. These correlations implicate an involvement of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease-related synaptic loss.
Figures


References
-
- Halliwell B. Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1992;59:1609–1623. - PubMed
-
- Halliwell B. Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: Therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging. 2001;18:685–716. - PubMed
-
- Faraci FM. Reactive oxygen species: Influence on cerebral vascular tone. J Appl Physiol. 2006;100:739–743. - PubMed
-
- Mantha AK, Moorthy K, Cowsik SM, et al. Neuroprotective role of neurokinin B (NKB) on beta-amyloid (25–35) induced toxicity in aging rat brain synaptosomes: Involvement in oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. Biogerontology. 2006;7:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Markesbery WR, Lovell MA. DNA oxidation in Alzheimer's disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:2039–2045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

