P38alpha-selective mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor for improvement of cultured human islet recovery
- PMID: 20084046
- PMCID: PMC2860020
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181c0dd8f
P38alpha-selective mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor for improvement of cultured human islet recovery
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated whether the recovery of cultured human islets is improved through the addition of a p38alpha-selective mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, SD-282, to clinically used serum-free culture medium.
Methods: Immediately after isolation, islets were cultured for 24 hours in medium alone (control) or medium containing dimethyl sulfoxide, 0.1 microM SD-282, or 0.3 microM SD-282. Cytokine expression, apoptotic beta-cell percentage, and islet function were assessed postculture.
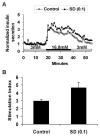
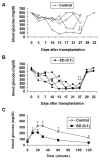
Results: Expression of p38 and phosphorylated p38 in islets increased during culture. Interleukin 6 mRNA expression in cultured islets, as well as IL-6, IL-8, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor released into the medium, was significantly reduced by adding SD-282. The apoptotic beta-cell percentage was significantly lower in islets cultured with 0.1 microM SD-282, but not 0.3 microM, as compared with the control. Stimulation indices measured in vitro were higher but without significance (P = 0.06); the function of transplanted islets in diabetic NOD-scid mice was also better in 0.1-microM SD-282 group as compared with control.
Conclusions: Better islet function was obtained by adding 0.1 microM SD-282 to the serum-free culture medium. This improvement was associated with suppression of cytokine production and prevention of beta-cell apoptosis. However, this beneficial effect was diminished at a higher concentration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improvement of human islet cryopreservation by a p38 MAPK inhibitor.Am J Transplant. 2007 May;7(5):1224-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01741.x. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Am J Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17331110
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is expressed in pancreatic islets from prediabetic NOD mice and in interleukin-1 beta-exposed human and rat islet cells.Diabetologia. 2001 Mar;44(3):325-32. doi: 10.1007/s001250051622. Diabetologia. 2001. PMID: 11317664
-
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor enhances human islet posttransplantation survival.Transplantation. 2011 Oct 15;92(7):745-51. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31822bc95a. Transplantation. 2011. PMID: 21869742 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of JNK and p38 stress activated protein kinases in isolated islets of Langerhans: insulin as an autocrine survival signal.Ann Surg. 2001 Jan;233(1):124-33. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200101000-00018. Ann Surg. 2001. PMID: 11141234 Free PMC article.
-
The sequential combination of a JNK inhibitor and simvastatin protects porcine islets from peritransplant apoptosis and inflammation.Cell Transplant. 2011;20(7):1139-51. doi: 10.3727/096368910X550170. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Cell Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21176401
Cited by
-
mRNA of the pro-apoptotic gene BBC3 serves as a molecular marker for TNF-α-induced islet damage in humans.Diabetologia. 2011 Aug;54(8):2056-66. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2183-8. Epub 2011 May 13. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21567299
-
Regulation of the CCL2 gene in pancreatic β-cells by IL-1β and glucocorticoids: role of MKP-1.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046986. Epub 2012 Oct 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056550 Free PMC article.
-
Use of additives, scaffolds and extracellular matrix components for improvement of human pancreatic islet outcomes in vitro: A systematic review.Islets. 2017 Sep 3;9(5):73-86. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2017.1335842. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Islets. 2017. PMID: 28678625 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of a proapoptotic gene (BBC3) in islet injury mediated by cold preservation and rewarming.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):E1016-26. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00441.2015. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27117005 Free PMC article.
-
Islet Culture/Preservation Before Islet Transplantation.Cell Med. 2015 Aug 26;8(1-2):25-9. doi: 10.3727/215517915X689047. eCollection 2015 Dec 17. Cell Med. 2015. PMID: 26858905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marzorati S, Pileggi A, Ricordi C. Allogeneic islet transplantation. Expert Opin Biol Ther Nov. 2007;7(11):1627–1645. - PubMed
-
- Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, et al. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes Jul. 2005;54(7):2060–2069. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006 Sep 28;355(13):1318–1330. - PubMed
-
- Ihm SH, Matsumoto I, Zhang HJ, Ansite JD, Hering BJ. Effect of short-term culture on functional and stress-related parameters in isolated human islets. Transpl Int. 2008 Oct 13; - PubMed
-
- Berney T. Islet culture and counter-culture. Transpl Int. 2008 Nov 1; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

