Methodological challenges of genome-wide association analysis in Africa
- PMID: 20084087
- PMCID: PMC3769612
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg2731
Methodological challenges of genome-wide association analysis in Africa
Abstract
Medical research in Africa has yet to benefit from the advent of genome-wide association (GWA) analysis, partly because the genotyping tools and statistical methods that have been developed for European and Asian populations struggle to deal with the high levels of genome diversity and population structure in Africa. However, the haplotypic diversity of African populations might help to overcome one of the major roadblocks in GWA research, the fine mapping of causal variants. We review the methodological challenges and consider how GWA studies in Africa will be transformed by new approaches in statistical imputation and large-scale genome sequencing.
Figures
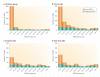
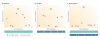
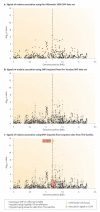
References
-
- McCarthy MI, et al. Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: consensus, uncertainty and challenges. Nature Rev. Genet. 2008;9:356–369. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly P. Progress and challenges in genome-wide association studies in humans. Nature. 2008;456:728–731. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Morris SS, Bryce J. Where and why are 10 million children dying every year? Lancet. 2003;361:2226–2234. - PubMed
-
- Mathers CD, Boerma T, Ma Fat D. Global and regional causes of death. Br. Med. Bull. 2009;92:7–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

