Structural biology of human H3K9 methyltransferases
- PMID: 20084102
- PMCID: PMC2797608
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008570
Structural biology of human H3K9 methyltransferases
Abstract
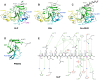
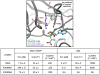
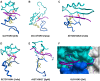
SET domain methyltransferases deposit methyl marks on specific histone tail lysine residues and play a major role in epigenetic regulation of gene transcription. We solved the structures of the catalytic domains of GLP, G9a, Suv39H2 and PRDM2, four of the eight known human H3K9 methyltransferases in their apo conformation or in complex with the methyl donating cofactor, and peptide substrates. We analyzed the structural determinants for methylation state specificity, and designed a G9a mutant able to tri-methylate H3K9. We show that the I-SET domain acts as a rigid docking platform, while induced-fit of the Post-SET domain is necessary to achieve a catalytically competent conformation. We also propose a model where long-range electrostatics bring enzyme and histone substrate together, while the presence of an arginine upstream of the target lysine is critical for binding and specificity.
Enhanced version: This article can also be viewed as an enhanced version in which the text of the article is integrated with interactive 3D representations and animated transitions. Please note that a web plugin is required to access this enhanced functionality. Instructions for the installation and use of the web plugin are available in Text S1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Computational characterization of substrate and product specificities, and functionality of S-adenosylmethionine binding pocket in histone lysine methyltransferases from Arabidopsis, rice and maize.Proteins. 2018 Jan;86(1):21-34. doi: 10.1002/prot.25399. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Proteins. 2018. PMID: 29024026
-
Heterodimerization of H3K9 histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP activates methyl reading and writing capabilities.J Biol Chem. 2021 Nov;297(5):101276. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101276. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34619147 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and specificity of the human SUV39H2 protein lysine methyltransferase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1849(1):55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25459750
-
A case study in cross-talk: the histone lysine methyltransferases G9a and GLP.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jun;38(11):3503-11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq081. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20159995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the multi-faceted role of the SUV family of H3K9 methyltransferases in carcinogenesis and cancer progression.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188498. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188498. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33373647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Division of labor between the chromodomains of HP1 and Suv39 methylase enables coordination of heterochromatin spread.Mol Cell. 2013 Jul 11;51(1):80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.06.013. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23849629 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent inhibition of NSD1 histone methyltransferase.Nat Chem Biol. 2020 Dec;16(12):1403-1410. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0626-6. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Nat Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32868895 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in EZH2 cause Weaver syndrome.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Jan 13;90(1):110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.018. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22177091 Free PMC article.
-
PRDM8 reveals aberrant DNA methylation in aging syndromes and is relevant for hematopoietic and neuronal differentiation.Clin Epigenetics. 2020 Aug 20;12(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13148-020-00914-5. Clin Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32819411 Free PMC article.
-
Human SETMAR is a DNA sequence-specific histone-methylase with a broad effect on the transcriptome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 10;47(1):122-133. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky937. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30329085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Grewal SI, Moazed D. Heterochromatin and epigenetic control of gene expression. Science. 2003;301:798–802. - PubMed
-
- Martin C, Zhang Y. The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:838–849. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, et al. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Lachner M, O'Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature. 2001;410:116–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

