Two plant viral suppressors of silencing require the ethylene-inducible host transcription factor RAV2 to block RNA silencing
- PMID: 20084269
- PMCID: PMC2800190
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000729
Two plant viral suppressors of silencing require the ethylene-inducible host transcription factor RAV2 to block RNA silencing
Abstract
RNA silencing is a highly conserved pathway in the network of interconnected defense responses that are activated during viral infection. As a counter-defense, many plant viruses encode proteins that block silencing, often also interfering with endogenous small RNA pathways. However, the mechanism of action of viral suppressors is not well understood and the role of host factors in the process is just beginning to emerge. Here we report that the ethylene-inducible transcription factor RAV2 is required for suppression of RNA silencing by two unrelated plant viral proteins, potyvirus HC-Pro and carmovirus P38. Using a hairpin transgene silencing system, we find that both viral suppressors require RAV2 to block the activity of primary siRNAs, whereas suppression of transitive silencing is RAV2-independent. RAV2 is also required for many HC-Pro-mediated morphological anomalies in transgenic plants, but not for the associated defects in the microRNA pathway. Whole genome tiling microarray experiments demonstrate that expression of genes known to be required for silencing is unchanged in HC-Pro plants, whereas a striking number of genes involved in other biotic and abiotic stress responses are induced, many in a RAV2-dependent manner. Among the genes that require RAV2 for induction by HC-Pro are FRY1 and CML38, genes implicated as endogenous suppressors of silencing. These findings raise the intriguing possibility that HC-Pro-suppression of silencing is not caused by decreased expression of genes that are required for silencing, but instead, by induction of stress and defense responses, some components of which interfere with antiviral silencing. Furthermore, the observation that two unrelated viral suppressors require the activity of the same factor to block silencing suggests that RAV2 represents a control point that can be readily subverted by viruses to block antiviral silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

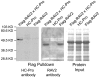

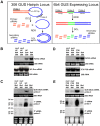


References
-
- Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, et al. Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006;9:436–442. - PubMed
-
- Kunkel BN, Brooks DM. Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 2002;5:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. - PubMed
-
- Ratcliff F, Harrison BD, Baulcombe DC. A Similarity Between Viral Defense and Gene Silencing in Plants. Science. 1997;276:1558–1560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

