Association of urinary bisphenol a concentration with heart disease: evidence from NHANES 2003/06
- PMID: 20084273
- PMCID: PMC2800195
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008673
Association of urinary bisphenol a concentration with heart disease: evidence from NHANES 2003/06
Abstract
Background: Bisphenol A (BPA) is a high production volume chemical widely used in food and drinks packaging. Associations have previously been reported between urinary BPA concentrations and heart disease, diabetes and liver enzymes in adult participants of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003/04. We aimed to estimate associations between urinary BPA concentrations and health measures in NHANES 2005/06 and in data pooled across collection years.
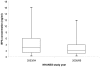
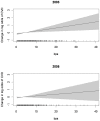
Methodology and findings: A cross-sectional analysis of NHANES: subjects were n = 1455 (2003/04) and n = 1493 (2005/06) adults aged 18-74 years, representative of the general adult population of the United States. Regression models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, education, income, smoking, BMI, waist circumference, and urinary creatinine concentration. Main outcomes were reported diagnoses of heart attack, coronary heart disease, angina and diabetes and serum liver enzyme levels. Urinary BPA concentrations in 2005/06 (geometric mean 1.79 ng/ml, 95% CI: 1.64 to 1.96) were lower than in 2003/04 (2.49 ng/ml, CI: 2.20 to 2.83, difference p-value = 0.00002). Higher BPA concentrations were associated with coronary heart disease in 2005/06 (OR per z-score increase in BPA = 1.33, 95%CI: 1.01 to 1.75, p = 0.043) and in pooled data (OR = 1.42, CI: 1.17 to 1.72, p = 0.001). Associations with diabetes did not reach significance in 2005/06, but pooled estimates remained significant (OR = 1.24, CI: 1.10 to 1.40, p = 0.001). There was no overall association with gamma glutamyl transferase concentrations, but pooled associations with alkaline phosphatase and lactate dehydrogenase remained significant.
Conclusions: Higher BPA exposure, reflected in higher urinary concentrations of BPA, is consistently associated with reported heart disease in the general adult population of the USA. Studies to clarify the mechanisms of these associations are urgently needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults.JAMA. 2008 Sep 17;300(11):1303-10. doi: 10.1001/jama.300.11.1303. Epub 2008 Sep 16. JAMA. 2008. PMID: 18799442
-
Trends and disparities in urinary BPA concentrations among U.S. emerging adults.Environ Res. 2019 Sep;176:108515. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.05.046. Epub 2019 May 30. Environ Res. 2019. PMID: 31195292
-
Use of NHANES data to link chemical exposures to chronic diseases: a cautionary tale.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051086. Epub 2012 Dec 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23227235 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphenol A and human health: a review of the literature.Reprod Toxicol. 2013 Dec;42:132-55. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Reprod Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23994667 Review.
-
Lead and bisphenol A concentrations in the Canadian population.Health Rep. 2010 Sep;21(3):7-18. Health Rep. 2010. PMID: 20973429 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolically Healthy Obesity-Heterogeneity in Definitions and Unconventional Factors.Metabolites. 2020 Jan 27;10(2):48. doi: 10.3390/metabo10020048. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32012784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism of Bisphenol A Atherogenicity Involves Apolipoprotein A-I Downregulation through NF-κB Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 12;20(24):6281. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246281. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31842455 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal bisphenol A exposure and maternally reported behavior in boys and girls.Neurotoxicology. 2014 Dec;45:91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Neurotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 25307304 Free PMC article.
-
Probabilistic integrated risk assessment of human exposure risk to environmental bisphenol A pollution sources.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Oct;23(19):19897-910. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7207-y. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27424203
-
Variation in urinary flow rates according to demographic characteristics and body mass index in NHANES: potential confounding of associations between health outcomes and urinary biomarker concentrations.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Apr;123(4):293-300. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408944. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 25625328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burridge E. Bisphenol A: product profile. European Chemical News. 2003:14–20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

